Fungus: Definition, Characteristics, Types and Economic Roles
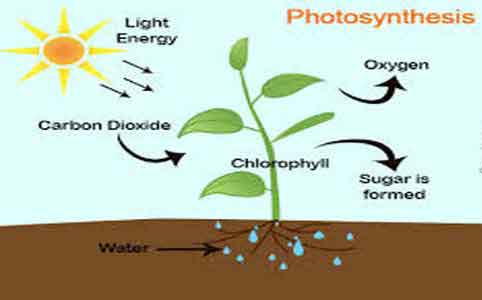
Fungi (singular fungus) are the eukaryotic organisms that belong to the Kingdom Fungi. They have no chlorophyll pigments and vascular tissues. The body consists of a single cell to branched filamentous hyphae that often produce specialized fruiting bodies. The special characteristic of fungi is that they grow rapidly and die soon. In nature, there are … Read more