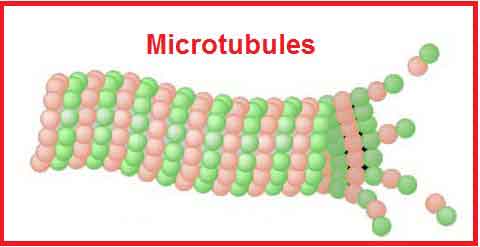
Non-membranous tubules are present in the eukaryotic cell`s cytoplasm. These tubules are hollow and ultrafine and their number is numerous in the cytoplasm. These tubules are made up of protein, known as tubulin which maintains the cell shape and plays an important role in the movement. Other proteins like Kinesin and dynein are also found in the microtubules. The combination of microtubules and microfilaments forms the cytoskeleton of the cell. Microtubules are responsible for the movement of the cell membrane, organelles, and cytoplasm.
The electron microscope has revealed that the cytoplasmic matrix of most eukaryotic cells contains microtubule and micro-filaments. In addition to this, the microtubules also occur in cilia, flagella, centrioles, and basal bodies, etc. and microfilaments are found in the axons of the neurons.
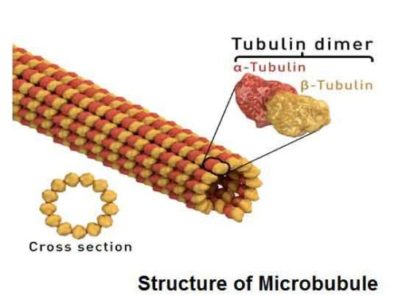
Microtubules are polymers of tubulin that have fine hollow cylinders of variable length. Generally, the microtubule consists of 13 protofilaments in the tubular arrangement. In some bacterial, microtubule consists of a ring of five protofilaments.
A microtubule can grow up to 50 µm in length and is highly dynamic. Tubules are very stiff in nature, and the outer diameter of a microtubule ranges from 23- 27 nm while the inner diameter from11-15 nm. The wall of the microtubule is about 60 Å in thickness and made up of alternating helix of α-tubulin and β-tubulin. Tubulin is a globular protein in nature. The α- and β-tubulins combine and form one dimer. Electron microscopic structure of cells has revealed that spindle fibers are created by the aggregation of much smaller fibers called microtubules.
Functions of Microtubules
- They form a supporting framework or cytoskeleton and give shape to the cell.
- They form the mitotic apparatus (spindles) consisting of bundles of microtubules.
- They help to make up the internal structure of flagella and cilia.
- They are related to the movement, such as the undulation of cilia and flagella.
- Microtubules are involved in the transport of macromolecules within the cells.
- During cell differentiation, cells change their shapes with the help of microtubules.
- They also take part in cell division. In this case, they make up the mitotic spindles as the major constituents.
- They are involved in various cellular processes, such as the movement of the secretory vesicles and organelles.