All types of cells are bounded by a thin, porous selectively permeable membrane which is known as the plasma membrane, cell membrane, plasmalemma or cytoplasmic membrane. It distinct the content of cell from the outside environment.
Carl Nägeli and Carl Cramer first discovered the term cell membrane in 1855 while Janet Quentin Plowe given the term plasmalemma in 1931. According to some Scientists, cell membrane originated from the endoplasmic reticulum. Plasma membrane lies between the cell wall and cytoplasm in the bacteria and plant cells and it is the outer limiting membrane of most animal cells.
Structure of Plasma Membrane
The plasma membrane is invisible and sometimes it contains brush border or sac-like structure, known as pinocytic vacuoles. If you observe it under an electron microscope, finger-like brush borders are available. They are known as microvilli. In between two adjacent cells, the plasma membranes become thicker in certain regions. From these areas, many fine filaments are seen, known as tonofilaments radiate towards the interior of the cell. Such thickened areas of the plasma membrane are known as desmosomes.
According to Dannielli and Davson (1935), the plasma membrane is about 75-80 Å in thick. The plasma membrane is composed of triple-layered structure. If you observe under a high magnification electron microscope, you will find double layer of lipid molecules 35 Å thick. Triple-layered structure of plasma membrane was discovered by J.D. Roberson in 1959. Two densely protein layers are also found in plasma membrane. In this case, thickness of each protein layer is 20 Å.
The lipid layers consist of most of the phospholipids. Its top end contains phosphate group and the tail end bears lipid group. In this case, phosphate group is positively charged while lipid group is negatively charged.

The Unit Membrane Model of Robertson
Also read: Cell Wall: Structure and Functions
The Fluid Mosaic Model of Plasma Membrane
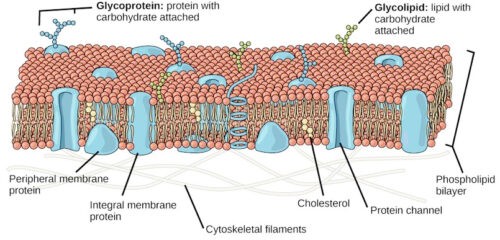
The lipid-globular protein mosaic model suggests, as the name implies, that instead of a continuous layer of protein on the surface of the membrane there is discontinuous mosaic globular protein. They remain partially embedded in and partially protruding from the phospholipid bilayer. There are also some discontinuous peripheral globular proteins arranged just outside and along the surface of the phospholipid bilayer.
This model was observed by English Scientists S. J. Singer and Garth Nicolson in 1972. This model is also known as Singer – Nicolson’s fluid mosaic model. According to this model, the plasma membrane looks like a mosaic which contains some components like phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins, and carbohydrates, etc. which gives the membrane a fluid character. Generally, the percentages of proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids in the plasma membrane vary with cell type. In myelin, the proportion of proteins and lipid are 18% and 76% respectively while the inner membrane of mitochondrial contains 76% protein and 24% lipid.
According to this theory, the main component of the cell membrane is a bimolecular lipid layer which actually consists of two rows of amphiphilic phospholipids molecules. Each phospholipid molecule contains three-carbon glycerol backbone with two fatty acid molecules which are attached to carbons 1 and 2 and a phosphate-containing group that is attached to the third carbon.

Fluid Mosaic Model of Plasma Membrane
Each phospholipid molecule has a water-soluble polar head and two fat-soluble non-polar tails. Top head of phospholipids is hydrophilic while tail end is hydrophobic. The phospholipid layer also contains protein and cholesterol. They make the plasma membrane look like a mosaic.
Chemically, the second major component of plasma membranes is proteins. Some protein molecules exist outside the lipid layer; called peripheral protein molecule and some are partially or entirely pass across the lipid layer, called integral protein molecules. Integral protein molecules create an ion channel through the cell membrane for passing water-soluble molecules. A single integral protein usually consists of 20–25 amino acids.
The third major component of plasma membranes is oligosaccharide molecules (carbohydrates). These oligosaccharide molecules attached to some protein and lipid molecules of the outer side of the cell membrane to form glycoprotein and glycolipid respectively. Generally, these carbohydrate chains contain 2–60 monosaccharide units which can be either branched or straight.
Chemical Composition of Plasma Membrane
Chemically cell membrane is made up of the following components:
- Protein (60-80%): Structural protein, carrier protein, enzymes, etc.
- Lipid (20-40%): Phospholipid, sterols, etc.
- Carbohydrates (4-5%): Oligosaccharides
- Water and minerals: Trace amount.
Functions of the Plasma Membrane
- The plasma membrane envelops the cytoplasm of living cells.
- It separates the internal components of the cell from the external environment.
- It protects the internal structure of the cell and different organelles of the cytoplasm.
- It maintains the shape of the cell.
- It helps to attach the cell with the extracellular matrix;
- It also helps to make cell group together to form tissues;
- It helps to regulate the transport of materials within the cells due to their selectively permeable characteristics.
- The cell membrane functions as a barrier that makes it possible for the cytoplasm to maintain a different composition from the material surrounding the cell.
- It provides protection to the internal contents of the cell.
- It can take in solid and liquid materials by phagocytosis and pinocytosis processes respectively.
- In animal cells, it is involved in the formation of vesicles, cilia, flagella, microvilli, etc.
- The cell membrane contains numerous receptors that are involved in communication with other cells and the outside world in general. These respond to antigens, hormones, and neurotransmitters in various ways.
- The cell membrane also allows cell identification.
- It enhances the absorbing area by producing microvilli in animal cells.
- It controls the molecular activity of the cell.
- It takes part in the formation of the endomembrane system.
- The cell membrane contains different types of enzymes.
- It plays important roles in developing different cell organelles.
- The plasma membrane of certain animal cells contains chemoreceptors which receive chemical stimulation.
- It helps in the transport system. The membrane contains some proteins and enzymes which are involved in the transportation of certain substances such as sugar, sodium and other ions, etc across the membrane.
- It also helps in the transport of selective materials from and to the cells.
- It plays a role in exosmosis and endosmosis.
- It also plays a role in endocytosis and exocytosis.
Also read: Cell Structure and Functions