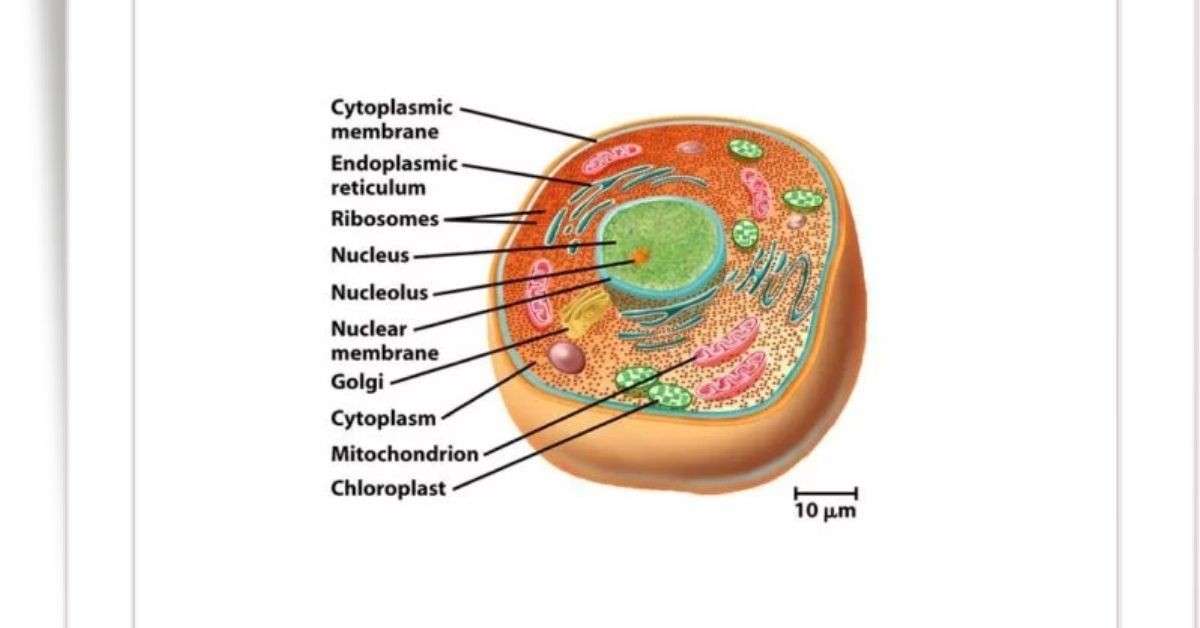
The cell is the structural and functional unit of life, which is also known as “building blocks of life.” The science which deals with the study of cells is referred to as Cytology or cell biology. Robert Hooke first discovered the cells in 1665. Matthias Jakob Schleiden and Theodor Schwann first developed a cell theory in 1839. Based on cell theory, all organisms are made from one or more cells. The word “cell” is derived from Latin words, cella, which means “small room.”
The cell contains cytoplasm with proteins and different nucleic acids, which is bounded by a membrane. Under a microscope, most animal and plant cells are visible, and their dimensions range from 1-100 µm. The number of cells varies from species to species. The human contains about 4×1013 cells. The smallest known cell is a tiny single-celled bacterium, known as Mycoplasma, which is 0.2 μm in diameter.
Definition of cell
There are various definitions of the cell which are given below:
- The structural and functional unit of living body is known as cell.
- The protoplasm surrounded by the membrane is known as cell.
- The smallest organized unit of the living body which is independent and self-reproducing under favorable condition, is known as cell (De Robertis and De Robertis, 1981).
- It is a unit of biological activity delimited by a semi-permeable membrane and capable of self reproduction in a medium free of other living system (Loewy and Sikevitz, 1969).
- The cell is the basic unit in which matter energy are acquired, converted, stored, utilized and also in which biological information is stored, manipulated and expressed (Swanson and Webster, 1978).
Number of Cell
The number of cell varies in the living organisms. The unicellular organisms like bacteria, amoeba, diatoms, Euglena etc contain single cell in their body but most of the plants and animals are multi-cellular organisms which contain many cell in their body. The number of the cell is never fixed for any multi-cellular organism.
Shape of the Cell
The shape of the cells varies from cell to cell. In general, the cell is spherical in shape in animal. In case of different animals and plants, the shape of the cell may be oval, elongated, triangular, cylindrical, cuboidal, rounded, polygonal or irregular. The size and shape of the cell correlates with its activities. The external and internal environment of the organism may also cause shape variations in the cell due to internal or mechanical stress or pressure and surface tension. The shape of the cell may vary from organ to organ, plant to plant and animal to animal.
Size of the Cell
The size of the cells varies from cell to cell. Most of the eukaryotic cells are microscopic in size but they are bigger than the bacteria. Generally, size of the cell varies from 1-175000 µm. Among the living organisms, the smallest cell is mycoplasma bacteria which are 0.1-0.25 µm in diameter while the biggest cell is ostrich egg (170 ×135 mm). The longest cell is the neuron cell which is about a meter or more in length.
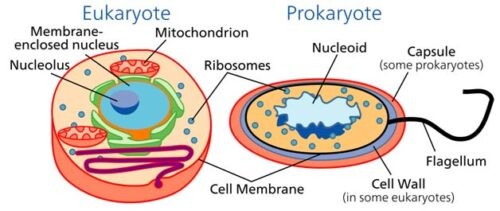
Types of Cell
Generally, the cell is of two types:
- Prokaryotic Cell
- Eukaryotic Cell
Eukaryotic cell (left) and Prokaryotic cell (right)
Prokaryotic Cell
This type cell is lack of nuclear envelop and well defined cytoplasmic organelles such as endoplasmic reticulum(ER), Golgi body, Mitochondria, centriole etc. Example of eukaryotic cells: Bacteria, blue green algae etc.
Most Important Characteristics of Prokaryotic Cell
- The prokaryotic cells are unicellular and filamentous like form which is not exceeding 10 µm in diameter.
- They have a more or less rigid cell wall and a jelly like mucilaginous capsule or sheath outside the plasma membrane.
- This cell does not contain nucleus due to absence of nuclear envelop.
- This type of cell also contain single naked chromosome with naked DNA.
- The cytoplasm of the prokaryotic cell does not contain well defined cell organelles such as endoplasmic reticulum(ER), Golgi body, mitochondria, centriole, vacuoles, lysosome, chloroplast etc.
- Most of the prokaryotic cells have motile organs such as cilia and flagella.
- They multiply by binary fusion.
Eukaryotic Cell
The eukaryotic cell has the nucleus with a definite nuclear membrane. This type of cell also contains cytoplasmic organelles like endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi bodies, mitochondria, lysosomes, etc.
Characteristic Features of Eukaryotic Cell
The eukaryotic cell is the true cell which has the following characteristic features:
- It is generally large in size, but only few cells being under 10 µm in diameter.
- The cell is bounded by the plasma membrane in the animal cell but in the plant cell, it is bounded by the cell wall which is made up of cellulose.
- This type of cell contains true nucleus which bears nucleoplasm, nucleolus, RNA, DNA, chromosomes and nuclear membrane.
- The eukaryotic cell also contains cytoplasmic organelles like endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi bodies, mitochondria, lysosomes, etc.
Cell Structure and Their Functions
The eukaryotic cells have different shapes, sizes and physiology but all the cells are typically composed of:
- Cell-covering
- Cytoplasm
- Cytoplasmic organelles, ergasitic substances and
- A true nucleus
Structure of a Typical Plant Cell
Cell-covering
Cell-covering has two parts such as plasma membrane and cell wall. Most of the cells are enclosed by a thin porous semi permeable membrane which is known as plasma membrane. The plasma membrane may be modified to form villi, cilia, flagella, cavities, and other special structures. The cell wall is present only in the plant cell. It is present outside of the cell membrane which is a thick semirigid, laminated, non-living cellulose covering.
Structure of Animal Cell
Functions of Cell Covering
Plasma membrane is a permeable membrane by which extracellular substances entered into the cell while the cell wall provides protection and support to the plasma membrane and cytoplasm.
Cytoplasm
The substance which occurs between the plasma membrane and nuclear membrane is called cytoplasm. It is made up of the matrix and the organelles. Matrix is an amorphous, translucent, homologous colloidal liquid which is known as hyaloplasm or cytoplasmic matrix.
Functions of Cytoplasm
Cytoplasmic matrix contains glycolytic enzymes and structural materials such as sugars, amino acids, water, vitamins, nucleotides etc. They carry out the instructions sent from the nucleus. They also provide sites for cellular activities.
Cytoplasmic Organelles
The organelles are the membrane-bound living structures of a cell which are situated within the cytoplasm. Generally, they perform various important biosynthetic and metabolic activities such as transportation, support, storage, reproduction, respiration etc. The eukaryotic cell contains the following organelles:
Golgi Body
It is very important organelle of the cell and is covered by a single smooth membrane of lipoprotein. It consists of cisternae, vesicles and vacuoles.
Functions of Golgi Body
It plays an important role for the transportation of materials within the cell. It forms secretary vesicles and lysosomes. They also form cell wall of the plat cell and plasma membrane.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
They are inter-connectin tubules and vesicles which are bounded by a single unit membrane. The membranes may be rough and smooth due to presence or absence of ribosomes.
Functions of Endoplasmic Reticulum
They maintain intracellular circulatory system. They act as synthetic and storage organs. They provide mechanical support to the cell by making cytoplasmic frame work.
Lysosomes
It is found only in the animal cell and it is a tiny spheroid particles which consist of hydrolytic enzyme. They are enclosed within the single lipoprotein membrane.
Functions of Lysosomes
They mainly take part in the intracellular digestion of food materials within the cell by the process of pinocytosis and phagocytosis.
Ribosomes
They are minute spherical non-membranous structures which consist of RNA and protein. They have two structural unequal sized subunits. The smaller subunit is called 40s subunit and a large subunit is called 60s subunit. They are located freely in the cytoplasm or remain attached to the surface of endoplasmic reticulum, nucleus etc.
Functions of Ribosomes
They provide sites for protein synthesis.
Mitochondria
It is filamentous or granular hollow type structure which is bounded by a double lipoprotein membrane. The inner granulated membrane is convoluted to form cristae and divides the mitochondria into two chambers, the outer chamber and matrix filled inner chambers.
Functions of Mitochondria
They are called power house of the body because they produce energy as ATP through Kreb`s cycle, electron transport chain, bet-oxidation of fatty acids etc.
Chloroplasts
It is a disc shaped chlorophyll containing organelle which is bounded by double membrane. It is only present in the plant cell. Within the inner membrane, stroma or matrix is present. Stroma contains small cylindrical structures called grana. Granum is a flattened vesicles which contains small structures or quantosomes.
Functions of Chloroplasts
They act as a storage for starch, pigments for photosynthesis. They help in the biosynthesis of food stuffs by the process of photosysnthesis.
Centrosomes
It is present only animal cell. It contains dense cytoplasm which is placed near the nucleus of the cell.
Functions of Centrosomes
It forms the spindle during the cell division and help in the movement of chromosomes.
Nucleus
Nucleus is the brain of the cell which is generally rounded in shape and is placed at the center of the cell. The typical nucleus consists of the following components:
Nuclear membrane: It is also known as nuclear envelope. It is a bilayer membrane which is made of lipids and the genetic material in eukaryotic cells. It encloses the nucleus where nucleo-cytoplasmic interchange takes place.
Nucleoplasm: It is clear like water substance which is present in the space between the nuclear membrane and nucleolus. It contains ribose sugar, phosphorus, protein, nuclic acid and nucleotides.
Nucleolus: It is a dense spherical body covered by single membrane which is present in the nucleoplasm. It mainly consists of nucleoprotein.
Chromosomes: In the nucleoplasm, a thread tike elongated structure is present which is known as chromosome. They appear only during the cell division.
Nucleus and its parts
Functions of Nucleus
- They act as a brain for the cell.
- They synthesize RNA, ribosome and ribosomal protein.
- Nuclear membrane makes partitions between nucleus and cytoplasm.
- They regulate the cellular process and bear the hereditary instructions.
You might also read: Cell Related Terms and Definitions