Definition
Mitochondrion (plural-mitochondria) is a rounded, rod-shaped or filamentous body. It is enclosed by double membrane. The term ‘mitochondria’ come from two Greek words such as ‘mito’ and ‘chondrion’. In this case, mito means thread while chondrion means granule. It is located in most of the cells and spreads all over the cytoplasm. It produces chemical energy as ATP in the cells.
History of Mitochondria
Scientist Kolliker (1850) first observed mitochondria in the striated muscle. Flemming (1882) named it as fila. Rechard Altmann (1897) referred to the mitochondria as Bioplasts. Carl Benda (1897) first called these organelles as mitochondria.
Distribution and occurrence
It is not found in the prokaryotic cell and matured circulated RBC. Generally they are evenly distributed in the cytoplasm. It is also found in the base of the proximal convoluted tubules of nephron. The number of mitochondria present in the cell depends on its activities. Plant cell contains less number of mitochondria than animal cell. A normal liver cell may contain 1000-1600 mitochondria while some oocytes may contain more than 300000 mitochondria. On the other hand, Microasterias algae contain only one mitochondrion
Structure of Mitochondria
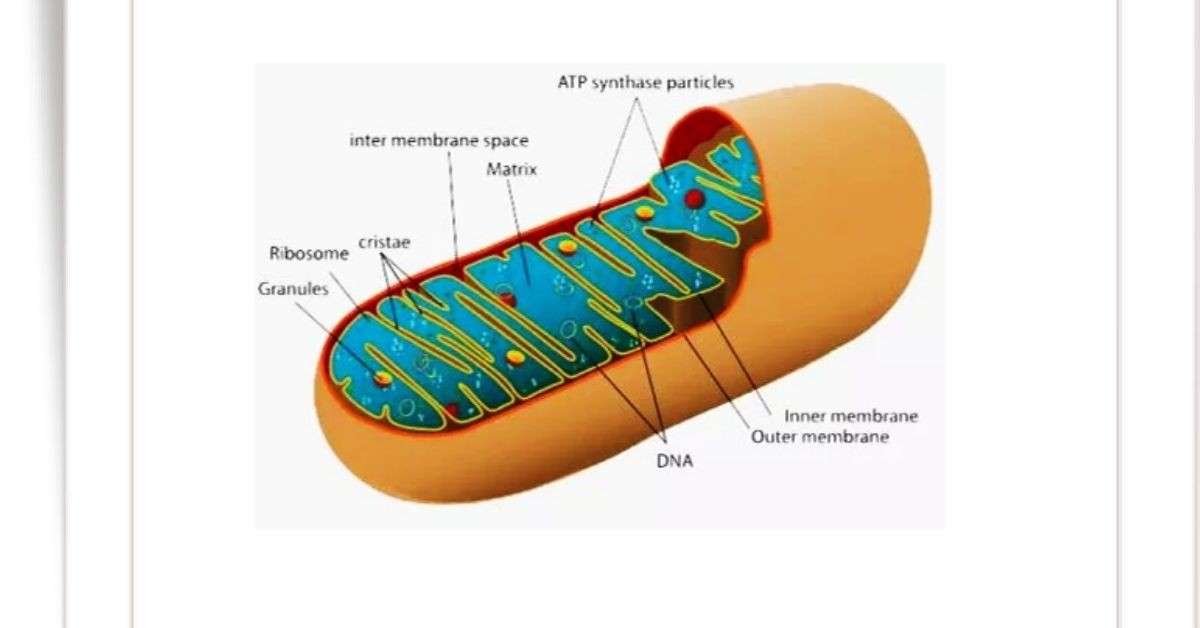
It is spherical or rod-shaped or filamentous body which grows about 3.0-7.0 µm in length and 0.2-2.0 µm in diameter. The body of the mitochondria is covered by two unit membranes such as outer and inner membranes. Lipo-protein is the main chemical component of each membrane and it is about 60 Å thick. Among the two membranes, outer membrane is smooth which surrounds the mitochondria but the inner membrane makes fold at different points and create incomplete barrier, known as cristae. 60-80 Å gap is present between the two membranes and this gap is filled up with fluid.
Chambers: It has two chambers, outer and inner chambers. The outer chamber is the space between the outer and inner membranes which is filled with watery fluid. The inner chamber is covered by the inner membrane. The inner chamber contains mitochondrial matrix.
Mitochondrial matrix: The inner chamber is filled with a relatively dense proteinaceous material usually called mitochondrial matrix. This matrix contains dense granules, ribosomes and mitochondrial DNA. The enzyme of the Krebs cycle is located in the matrix.
Mitochondrial particles
The cristae are bounded by mushroom-like substances (85 Å) and it protrudes into the matrix as a incomplete septa. Among these substances or particles, each contain three parts such as head, stem and base. On the cisternae, each particle is placed about 100 Å interval. Here, the particles have several names such as elementary particles, Fernandez-Moran subunits or F1-Particles.
Functions of Mitochondria
- It acts as a power house– Different enzymes present in the mitochondria help in oxidative phosphorylation and is thus site for formation of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP is high energy-rich substrates which supply 95% energy to the cell.
- Cell Respiration– Mitochondria are the respiratory organelles of the cell. Cell respiration includes glycolysis, oxidation of pyruvic acid, Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation.
- Oxidation of fat– Fatty acids of fats are oxidized at their β-position in the mitochondria.
- Syntheses of lipid– A set of enzymes that control synthesis of phospholipids are present in the mitochondria. These enzymes help in the formation of the phospholipids.
- Syntheses of protein– The mitochondrial matrix contain DNA which helps to synthesize RNA. This RNA and ribosome help for the formation of protein.
- Mitochondria help to maintain proper concentration of calcium ions in the cell.
- It helps to build certain parts of blood and hormones such as testosterone and estrogen.
Also read: Cell Nucleus: Definition, Structure and Functions