Gibberellin
The gibberellin is the plant hormone that contains diterpenoids organic acid and acts as growth regulator of the plants. The fungus Gibberella fujikuroi is responsible for fooling seedling disease or bakanae disease. Eiichi Kurosawa ( a Japanese scientist) first identified this disease in 1926. Later on, Tokyo University showed that this fungus Gibberella fujikuroi produces a substance which can cause bakanae or foolish disease and as a result, they given name the substance “Gibberellin”. Brian in England and Stodole in USA have discovered 3 different compounds like gibberellinA1, gibberellin A2 and gibberellic acid (GA3). More than 40 different gibberellins have been isolated.
Gibberellins generally occur naturally in the maturing seeds, germinating seedlings and growing tissues of expanding cotyledon or leaf.
Gibberellins (GA3) are colorless aesthetic acids and its chemical formula is (C19H22O6).
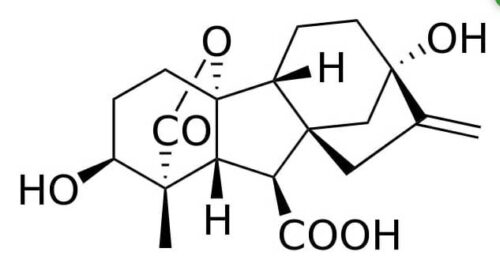
Chemical Structure of Gibberellin
Gibberellins are transported in all direction from their site of source. It is synthesized from acetate via mevalonate and geranyl geraniol.
Functions of Gibberellins
- Giberrellins increase the number and size of the cells.
- It promotes internodal growth of the plants.
- It helps to increase the size of leaves and fruits.
- By eliminating dormancy of seed, it influences the seed germination.
- It helps to produce parthenocarpic fruits.
- It helps to eliminate genetic dwarfism in plants.
- It induces the synthesis of hydrolytic enzymes such as amylase, protease, etc,. during seed germination.
- It helps in cell division and cell elongation.
- It also helps in flowering, fruiting and seed formation.
Cytokinin
Cytokinin is the alkaline plant hormone that contains furfuryl amino purine which helps in cell division. It is an important plant growth hormone. Folke Skoog discovered the effect of this hormone in 1940. Miller et al., (1956) first isolated a group of active substance from yeast DNA which can stimulate cell division in plants. These substances have been named as Kinetin because of their specific effect on cytokinesis. Later on, the term cytokinin is universally used to denote those substances which promote cell division.
This hormone is not in acidic in nature like auxin and gibberellins. It is alkaline and is transported to distance places of the plant body before it functions or may be active of the site of synthesis.
Cytokinins in combination with auxins strongly stimulate mitotic cell division in the meristematic tissues of the plant body. These are water soluble and can be transported in all direction of the plant body.
Most of the cytokinins have been isolated from fruits like tomatoes, apples, bananas, etc., and endosperm tissues. It is found abundantly in coconut milk. Corn seed contains cytokinin which is called zeatin. Such substances are also present in fruits and vegetative tissues.
Chemically it is 6-furfuryl amino purine which contains carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen and oxygen. The chemical formula is C10H9N5O.
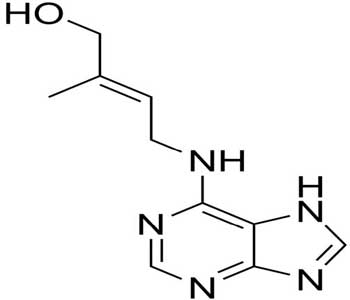
Chemical Structure of Cytokinin
Functions of Cytokinin
- Cytokinin helps to enlarge of cells.
- It promotes in cell division
- It helps to influence the normal development of embryo.
- It can enhance the protein synthesis.
- It also enhances the synthesis of RNA and other substances.
- It helps to encourage the development of buds.
- The senescence of leaves is delayed due to action of gibberellins.
- It can delay the ageing of plants.
- The germination of seed is stimulated by gibberellins.
- It helps to control immature shedding of leaf, flower and fruit.
- It helps in development of proplastid into plastid.
- It helps to delay the destruction of chlorophyll of the detached leaves.
