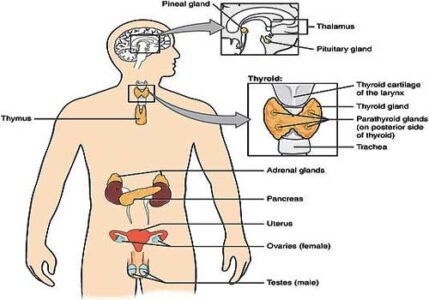
There are two types of glands in the body such as endocrine glands and exocrine glands. Endocrine glands are also known as ductless glands that constitute the endocrine system. The endocrine system forms network in the body and produce hormones directly into the blood stream. Endocrine glands perform various functions in the body. They influence the metabolism, reproduction, growth and so on. If endocrine gland does not work properly, it may cause various problems in your body.
In human body, the major endocrine glands include:
- 1. Hypothalamus
- 2. Pituitary gland
- 3. Adrenal gland
- 4. Parathyroid gland
- 5. Thyroid gland
- 6. Thymus gland
- 7. Pancreas
- 8. Pineal gland
- 9. Ovary
- 10. Testis
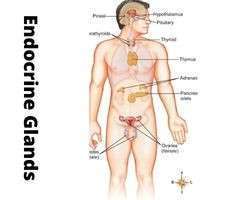
The endocrine glands, hormones and their major functions are described in the following table:
| Name of Hormones | Endocrine Glands | Functions |
|---|---|---|
| Growth Hormone Releasing Hormone (GHRH). | Hypothalamus | It helps to release of Growth Hormone (GH). |
| Thyrotrophin Releasing Hormone(TRH) | Hypothalamus | It helps to release of Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) and release of prolactin (PRL). |
| Corticotrophin Releasing Hormone(CRH) | Hypothalamus | It helps to release of Adreno Corticotrophic Hormone (ACTH). |
| Gonadotrophin Releasing Hormone(GnRH) | Hypothalamus | It helps to release of Luteinizing Hormone (LH) and Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH). |
| Somatostanin(SS) | Hypothalamus | It inhibits to secrete of growth hormone(GH) |
| Dopamine (DA) | Hypothalamus | It inhibits to secrete of prolactin (PRL). |
| Human Growth Hormone(HGH) or Somatotropic Hormone(STH) | Pituitary Gland | It controls growth of tissue, bone, muscles and internal organs.
It influences metabolic process. It also breaks down stored glycogen from the muscle and liver. |
| Thyroid Stimulating Hormone(TSH) | Pituitary Gland | It stimulates the secretion of thyroxin from the thyroid glands.
It controls intake of iodine by the thyroid gland. |
| Adreno Corticotrophic Hormone(ACTH) | Pituitary Gland | It stimulates the adrenal cortex and regulates the secretion from the adrenal glands.
It also influences the production of melanocyte. |
| Luteinizing Hormone(LH) | Pituitary Gland | It stimulates the testes to secrete testosterone or endrogene hormone.
It is responsible for formation of the corpus luteum, production of progesterone in females. |
| Follicle Stimulating Hormone(FSH) | Pituitary Gland | It influences the production of sperm by the seminiferous tubules of the testes in males.
It controls the development of grafian follicles(ova) in females. |
| Luteotrophic Hormone(LTH) | Pituitary Gland | It stimulates the development of breast and lactation in females.
It influences the development of secondary sexual characteristics in males and females. |
| Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone(MSH) | Pituitary Gland | It controls the pigments in melanocytes and thus determines skin color. |
| Anti Diuretic Hormone(ADH) or Vassopressin | Pituitary Gland | It increases the blood pressure.
It stimulates the kidney to reabsorb more water, preventing excessive water loss by urination. |
| Oxytocin | Pituitary Gland | It causes contraction of the uterus in females during childbirth and regulates lactation. |
| Thyroxine(T4) | Thyroid Gland | It increases metabolism of iodine, proteins and carbohydrates.
It increases cardiac output and heart rate. It increases milk production. |
| Tri-iodothyronine (T3) | Thyroid Gland | It increases metabolic rate of iodine.
It increases the sensitivity of nervous system. |
| Thyrocalcitocin | Thyroid Gland | It increases calcium absorption capability of bones.
It influences the metabolism and transportation of phosphate. |
| Parathyroid hormone (it is also known as parathormone or parathyrin) | Parathyroid Gland | It breaks down the bone and causing calcium release.
It increases the ability of the body to absorb calcium from food. It also increases the ability of kidney to held on calcium. |
| Thymosin | Thymus gland | It influences the formation of lymphocytes and antibody.
It helps in deposition of minerals in the bones. |
| Glucocorticoids or cortisol | Adrenal gland | It influences the synthesis of glycogen in muscle and liver.
It increases absorption rate of glucose and lipids from the intestine. |
| Mineralocorticoids or aldosterone | Adrenal gland | It increases the NaCl and water absorption capacity of kidney.
It increases the plasma content of the blood. It also increases the excretion rate of potassium (K). |
| Gonadocorticoids | Adrenal gland | It regulates the sex differentiation of the embryo.
It helps to develop of sex glands, gonads and secondary sex characteristics. |
| Epinephrine or Adrenaline | Adrenal gland | It increases the heart rate, blood pressure and carbohydrate metabolism rate.
It decreases the urine production rate. |
| Norepinephrine or Noradrenaline | Adrenal gland | It maintains a constant blood pressure by stimulating certain blood vessels to constrict when the blood pressure falls bellow normal |
| Insulin | Pancreas | It increases the metabolic rate of glucose to decrease it levels in the blood.
It increases the glycogen synthesis rate of liver and muscle. |
| Glucagon | Pancreas | It increases the activities of α-cells and β-cells.
It decreases the secretion rate of digestive gland. |
| Somatostanin | Pancreas | It inhibits the activities of α-cells and β-cells. |
| Gastrin | Gastrointestinal glands | It helps to secrate the pepsinogen and HCl. |
| Secretin | Gastrointestinal glands | It stimulates the pancreas and bile ducts to release sodium bicarbonate to neutralize the acid. |
| Cholecystokinin (CCK) | Gastrointestinal glands | It stimulates the release of digestive enzymes in the pancreas.
It also stimulates the contraction of the gall bladder to empty bile into the duodenum. |
| Gastric inhibitory peptide(GIP) | Gastrointestinal glands | It decreases the stomach contractions churning the chime, and slows the emptying of the stomach into the duodenum. |
| Enterocrinin | Gastrointestinal glands | It stimulates the intestine to secrete its own intestinal juice. |
| Peptide YY (PYY) or it also known as peptide tyrosine tyrosine | Gastrointestinal glands | It helps to slow down the passage of food along the gut. |
| Enterogastrone | Gastrointestinal glands | It inhibits the motility and acid secretion of stomach. |
| Melatonin | Pineal gland | It plays an important role to regulate sleep patterns.
It regulates the body’s daily (circadian) clock. |
| Testosterone | Testis | It helps in maturation and functional maintenance of male reproductive tract.
It helps in the development of secondary sex characters. It influences sex behavior. |
| Estrogen | Ovary | It helps in maturation and cyclic fluctuation of female reproductive tract.
It helps in the development of secondary sex characters. It stimulates duct system of mammary gland. It influences sex behavior. |
| Progesterone | Ovary | It regulates the female tract with the help of estrogen.
It develops alveolar system of mammary gland. It helps to prepare uterus for implantation of blastocyst. It helps in maintenance of blastocyst. |
| Relaxin | Ovary | It helps to maintain cervical tone.
It facilitates parturition. |
Some Endocrine System Disorders
Sometimes, endocrine glands produce too high or too low levels of hormones that have number of effects on our health. There are many conditions that occur due to cause of endocrine glands disorders. Among them some important disorders are described below briefly:
Cushing’s disease
This disease occurs if endocrine gland produces high level of hormone, cortisol. It shows the following symptoms:
- Increasing body weight;
- Fatty deposits occur in the face, shoulders;
- Weakening of muscles and bones;
- Irregular of periods in females;
- Purple stretch marks on the arms, thighs, and abdomen;
- Skin becomes thin that bruises easily;
- High blood pressure;
- Red cheeks;
- Growth of excess hair on the face, neck, chest, thighs and abdomen;
- Healing occurs slowly if cuts, scrapes, insect bites and infection;
- Decreasing sex drive and fertility in males.
- Disorders of mood and behavior;
- Severe fatigue;
- Headache;
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism occurs if thyroid gland secretes more hormones than necessary. Some general symptoms of hyperthyroidism include:
- Loss of weight;
- Rapid heartbeat;
- Nervousness, anxiety and irritability;
- It makes sleeping problem;
- Increasing appetite;
- Changing menstrual cycles;
- Fatigue;
- Weakness of muscles;
- Increasing sensitivity to heat;
- Thinning of skin;
- Sweating;
- Diarrhea, etc.
Hypothyroidism
It occurs due to secrete less thyroid hormone. Some general symptoms of Hypothyroidism include:
- Increasing the body weight;
- Fatigue;
- Dry and rough pale skin;
- Weakness;
- Loss of memory;
- Dry and coarse hair;
- Constipation;
- Loss of hair;
- Slow heart rate;
- Irregular menstrual cycle;
- Depression;
- Much sensitivity to cold;
- Swelling of thyroid gland;
Addison Disease
It is also known as adrenal insufficiency. It occurs if adrenal gland produce insufficient cortisol and aldosterone. All age groups and both sexes suffer from addison`s diseases ant it can be life-threatening. Addison`s diseases show some common symptoms which include:
- Weakness of muscle;
- Severe fatigue;
- Loss of weight;
- Decreasing appetite;
- Low blood pressure;
- Abdominal pain;
- Skin darkness;
- Low blood sugar level;
- Diarrhea or vomiting;
- Decreasing heart rate;
- Hair loss;
- Lesion in the mouth;
- Irritability;
- Depression;
- Energy loss;
- Irregular menstrual cycle;
- Sleep disturbances, etc;
Acromegaly
It happens if pituitary gland produces too much growth hormone (GH). Generally, a middle-aged person suffers from acromegaly disease. As a result, bones of hand feet and face increase in size. Some common symptoms of acromegaly include:
- Enlargement of feet and hands;
- Enlargement of facial features;
- Weakness of muscles;
- Tiredness;
- Enlargement of vocal cords and sinuses;
- Thickened oily skin;
- Headache;
- Enlargement of tongue;
- Too much sweating;
- Weakening of vision;
- Irregular menstrual cycle;
- Sexual dysfunction; etc.;
Diabetes
It happens due to high blood sugar level. It occurs if pancreas does not produce necessary amount of insulin. Some common symptoms of diabetes include:
- Weight loss;
- Tiredness;
- Increasing thirst or hunger;
- Frequent urge to urinate;
- Irritability, etc.