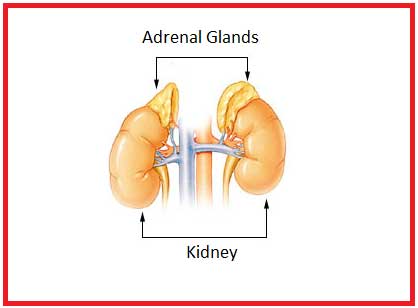
The adrenal gland is one kind of endocrine gland, which is also known as a suprarenal gland. It is two in number that is placed on the upper pole of each kidney at the level of 1st lumbar vertebra. The right adrenal gland of humans is pyramidal in shape, while the left adrenal gland is crescent-shaped and slightly larger than the right adrenal.
Each gland measures about 3 cm in width, 5 cm in length and about 1 cm in thickness, which is surrounded by the fibrous capsule. It surrounds the kidney. In the adult human body, the combined weight of the two glands ranges from 7-10 grams. It is yellowish in color. The adrenal gland consists of two parts, the outer cortex and inner medulla.
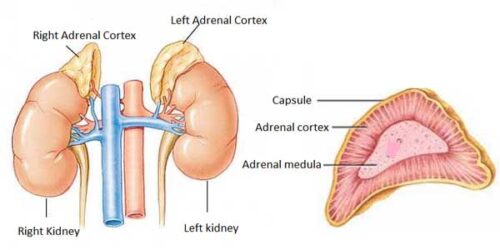
Image Showing Adrenal Gland and Its Various Parts
Adrenal Cortex
It is the outermost layer of the adrenal gland. This gland produces some essential hormones such as aldosterone, cortisol and androgens. The cortex consists of polyhedral epithelioid cells which are arranged in three layers:
1. Zona Glomerulosa: It is the outermost zones which are located just under the fibrous capsule of the gland. This outer layer produces a mineralocorticoid hormone, such as aldosterone. Generally, it is secreted by the activity of the aldosterone synthetase enzyme. This hormone helps to regulate long term blood pressure.
2. Zona Fasiculata: It is the middle layer which is located between the zona reticularis and the zona glomerulosa. This layer is the largest layer among three layers, which accounts for about 80% of the cortex. Cells in this layer are arranged in columns and contain lots of lipid droplets, smooth endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and mitochondria. Glucocorticoids such as cortisol hormones are produced from this layer.
3. Zona Reticularis: It is the inner irregular network rows of the cell layer. It is placed directly adjacent to the madula. This layer contains small cells with a small amount of cytoplasm and lipid droplets. It also contains some lipofusion pigment. It produces hormones like androgens.
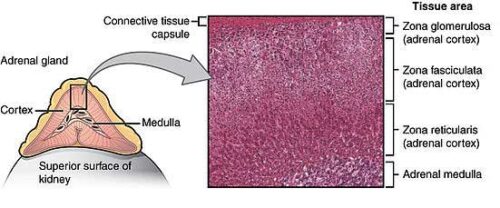
Image Showing Zones of Adrenal Cortex
Hormones of Adrenal Cortex
A number of cortical hormones are secreted from the cortex. They are grouped into three types:
Glucocorticoids: These groups of hormones are mainly secreted from zona fasiculata. They include cortisol, cortisone, corticosterone.
Minerelocorticoids: This group of hormones is secreted mainly from the zona glomerulosa. They include aldosterone and deoxycorticosterone (DOC).
Sex steroids: This group of hormones is secreted mainly from zona reticularies. They include androgen, estrogen, progesterone, etc.
The Functions of Adrenal Cortex
Effect on Carbohydrate Metabolism: Glucocorticoids help for the metabolism of carbohydrates as follows:
- It increases the formation of glycogen in the liver and muscles.
- It helps to increase the formation of glucose from protein and fat in the liver.
- It also helps to increase glucose absorption from the intestine.
- It helps to decrease glucose uptake by the tissues.
- It helps to increase the sugar level in the blood.
Effect on Minerals and Water Metabolism: Mineralocorticoids increase reabsorption of NaCl, bicarbonates, and water. It depresses of potassium and phosphate reabsorption by the renal tubules.
Effect on Protein Metabolism: Glucocorticoids break down tissue protein into amino acids; thus, body proteins are lost, and nitrogen excretion increases.
Effect on Fat Metabolism: Glucocorticoids increase the fat absorption from the intestine. They also increase lipid and cholesterol levels in the blood and decrease the synthesis of lipids from carbohydrates.
Effect on different System: Glucocorticoids decrease the number of eosinophils and lymphocytes in the blood. They regulate the composition of blood, blood volume, blood pressure, etc. It also controls bone formation, muscular activities, the function of the nervous system and the digestion system.
Adrenal Medulla
The vital part of the adrenal gland is known as the medulla, which is surrounded by the adrenal cortex. It consists of densely packed polyhedral cells that are surrounded by blood tissue. These cells are known as chromaffin cells. The adrenal medulla produces catecholamine adrenaline and noradrenaline hormones.
This organ can produce about 80% adrenaline or epinephrine and 20% noradrenaline or norepinephrine. These are protein hormones. Epinephrine (adrenaline) and nor-epinephrine together called catecholamines that are produced from the adrenal medulla and nerve endings such as sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves.
Functions of Epinephrine
- Epinephrine helps to increase conductivity, contractility, heart rate and cardiac output, etc.
- It helps to constrict all blood vessels, but it dilates coronary vessels and vessels of skeletal muscles
- It helps to increase the blood pressure and heart rate through the constriction of blood vessels.
- Epinephrine can cause dilation of bronchioles and increase the rate and depth of respiration.
- It helps to increase the excitability, contractibility and tone of skeletal muscle. It also causes a delay in fatigue.
- It helps to inhibit the tone of the involuntary muscles, which are found in the stomach, intestine and bronchiole.
- It also helps to inhibit intestinal movement and cause the construction of spleen, dilatation of the pupil, etc.
- It constricts the erector pilorum (muscle of skin), which causes the erection of hairs.
- It constricts cutaneous vessels, thus decreases the flow of blood, which prevents loss of body temperature.
- It increases the renal circulation; as a result, decrease the urine volume.
- It helps to increase the blood sugar by stimulating the breakdown of liver glycogen, the formation of glucose from lactic acid, etc.
- It also stimulates the secretion of saliva, lacrymal secretion, sweat secretion, etc.
Functions of Nor-epinephrine
Nor-epinephrine is also known as noradrenaline. Chemically, it is catecholamine and phenethylamine. It acts as a chemical messenger and transmits signals across nerve endings. It releases higher levels during the situation of stress or danger. Generally, it secretes the lowest amount during sleep and increases during wakefulness.
- It encourages vigilance and enhances restlessness and anxiety.
- It can cause an increase in blood pressure and heart rate.
- It causes the release of glucose and increases blood flow to skeletal muscles.
- It also decreases the level of blood flow to the gastrointestinal system.
- It helps to increase tear production and make the eye moist.
- It increases the number of blood pumps in the heart.
- It increases blood pressure through the constriction of blood vessels.
- It helps to release of rennin in the kidney and maintain the level of sodium in the bloodstream.
- It helps to generate body temperature.
- It helps to increase glucose production in the liver, which helps to increase energy sources.
- It helps to increase glucose uptake in the skeletal muscle.
- It helps to increase glucagon in the pancreas, which increases glucose production by the liver.
- It helps to increase the fat conversion to the substrate in the adipose tissue. These substrates use as an energy source by various tissues and muscles.
- It deduces the digestive activity in the stomach and intestine by the inhibitory effect of this hormone.
- It increases the level of circulating free fatty acids.
- Clinically, norepinephrine is used to maintain blood pressure in certain types of shocks.
Disorders and Diseases of the Adrenal Glands
There are multiple disorders and diseases caused by the adrenal glands when it does not work precisely. The following most common disorders and diseases of the adrenal glands are:
Addison’s Disease
It is caused due to hyposecretion or insufficient secretion of cortisol hormone.
Symptoms
- Pigmentation in the skin.
- Loss of muscular weakness.
- Loss of appetite.
- Vomiting.
- Diarrhea.
- Fall of blood pressure.
- Hypoglycemia.
- Nausea
- Reduction of fluid and blood volume.
- Low body temperature
- Renal insufficiency.
- Fatigue;
- Abdominal pain;
- Weight loss;
- Dizziness upon standing;
- Depression of sexual activity, etc.
Over production or hyper-functions of adrenal cortex causes the following diseases:
Cushing`s Syndrome
It is caused by over secretion of cortisol hormone. There are the following many symptoms of cushing`s syndrome:
- Moon face or rounded face due to deposition of fat on nose;
- Fish-like mouth with buffalo neck;
- Excessive hair growth in male;
- Masculinisation with growth of beard and moustache in female;
- Wasting of muscle;
- Osteoporosis of bones;
- Hypertension;
- Hyperglycemia;
- Increasing of Na+ and decreasing of K+ in plasma;
- Mental derangement, etc.
Adrenogenital Syndrome
It is caused due to the excessive secretion of adrenal androgen. It shows the following symptoms:
Symptoms of Adrenogenital Syndrome in Female:
- Deepening voice;
- Growth of beard,
- Increasing growth of muscle, etc;
Symptoms of Adrenogenital Syndrome in Male
- Feminization;
- Development of breast;
- Atrophy of testis, etc.