The sinus infection is known as sinusitis. It is a major health problem which can cause inflammation of the sinus tissues. The people that have weak immune systems are at greater risk to sinusitis.
Slimy substances are produced from sinuses, called mucous that help to keep the nasal passage moist. It also helps to trap different types of bacteria and dirt particles. In many cases, sinuses are filled or blocked with various infectious particles such as viruses, bacteria and fungi and can cause infection, known as sinusitis.
You might also read: Syphilis: Causes, Types, Symptoms and Treatment
There are the following four main sinuses:
- The maxillary sinus: It is situated in each cheekbone.
- The frontal sinus: It is placed on either side of forehead.
- The ethmoid sinus: It is located just behind the bridge of the nose.
- The sphenoid sinus: It is found between the upper part of the nose.
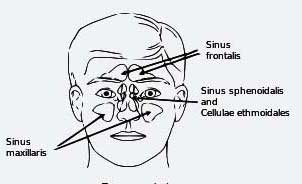
Image Showing Sinuses (Sinusitis): Image credit-wikipedia
Types of Sinusitis
Sinusitis is of the following two types:
- Acute sinusitis: It is sudden cold-like symptoms which can cause facial pain or stuffy nose. It can last 10 to 14 days but if you are affected by acute sinusitis then it normally continues 4 weeks or less.
- Chronic sinusitis: It is a condition which can cause sinus inflammation and it lasts for 8 weeks or more.
Causes of Sinusitis
It is often caused by an infection of the mucous membrane with a virus, bacteria, or fungus. Most people with acute sinusitis have a vital infection such as the common cold. Irritants and allargens can inflame the linings of nose and sinuses, causing sinusitis. Some irritants due to sinusitis include:
- Airborne allergens such as grass and trees pollen;
- Smoke and air pollution;
- Sprays containing chemicals such as household detergents;
Symptoms of Sinusitis
- Facial pain/pressure;
- Nasal stuffiness;
- Nasal discharge;
- Loss of smell;
- Cough/ congestion;
- Fever;
- Double vision or other vision changes;
- Bad breath;
- Fatigue;
- Dental pain;
- Cough or throat clearing;
- Nasal obstruction/blockage;
- Pus in the nasal cavity;
- Swelling or redness around your eyes;
- Nasal discharge/discolored post nasal drainage;
- Swelling around your cheeks, eyes, nose or forehead;
- Reducing sense of smell and taste;
- Ear pain;
- Confusion;
Complications
Children are affected more than adults by sinusitis. If you are severe affected by sinusitis, antibiotics are used to relieve and control the sinusitis. In many cases, infection can spread nearby face bone or the area around the eye. The brain is also infected by sinusitis which leads to meningitis.
Risk factors
Some risk factors due to chronic Sinusitis:
- Nasal polyps;
- A deviated septum;
- Aspirin sensitivity;
- Asthma;
- A dental infection;
- It may also cause AIDS/HIV or cystic fibrosis;
- Hay fever or another allergic condition;
Treatments
- A vaporizer or inhaling stream from a pan of boiling water may also help to relieve sinusitis;
- If you use saline nose drop which helps to recover sinusitis;
- Nasal drops are also useful to control sinusitis;
- Antibiotics or oral steroids may also be prescribed;
- Surgery should be considered only if medical fails or if there is a nasal obstruction that cannot be corrected with medications;
- You should avoid cigarette smoke and polluted air;
- You should avoid upper respiratory infections;
