The nerves of the brain which directly emerge from or enter the skull or the cranium including the brainstem are called cranial nerves. They transmit or relay various information between the different parts of the body and the brain. The main functions include special senses of vision, smell, taste, and hearing. They come out from CNS (central nervous system) above the level of the first vertebrae of the vertebral column.
There are twelve pairs of cranial nerves in mammals including human, each of which is denoted by Roman Number. Each cranial nerve is situated on both sides. Among 12 pairs, some are purely sensory, some are purely motor and the others are mixed. The first two pairs emerge from the cerebrum; the remaining ten pairs emerge from the medulla obolongata.
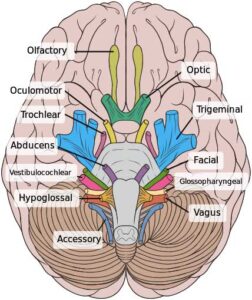
Image Showing Cranial Nerves: Image credit-Wikimedia commons
The 12 pairs cranial nerves are shown in the following table:
| Serial No | Name of Cranial Nerves |
|---|---|
| I | The olfactory nerve |
| II | The Optic Nerve |
| III | The Oculomotor Nerve |
| IV | The Trochlear Nerve |
| V | The Trigeminal Nerve |
| VI |
The Abducens Nerve |
| VII |
The Facial Nerve |
| VIII |
The Auditory Nerve |
| IX |
The Glossopharyngeal Nerve |
| X | The Vagus Nerve |
| XI |
The Accessory Nerve |
| XII |
The Hypoglossal Nerve |
Origin of the Cranial Nerves
The first two cranial nerves such as olfactory nerve I and the optic nerve II originate from the cerebrum while the cranial nerves III – XII arise from the brain stem.
12 pairs of cranial nerves, their nature, distribution and functions are described below:
I. Olfactory
Nature: Pure Sensory nerve
Origin and Distribution: It is originated from the olfactory lobe of cerebrum and extended to the mucus membrane of the nazal cavity. It is capable of regeneration.
Functions: It transmits the sense of smell from the nasal cavity.
II. Optic
Nature: Sensory nerve
Origin and Distribution: It is originated from the optic lobe of the midbrain and extended to the retinal wall of the eye.
Functions: It carries visual information from the retina of the eye to the brain.
III. Oculomotor
Nature: Motor nerve
Origin and Distribution: It is originated from the ventro-lateral side of the midbrain and innervates the eye muscles.
Functions: It controls the movements of eye muscles. It also helps the constriction of the pupil, and regulates an open eyelid
IV. Trochlear
Nature: Motor nerve
Origin and Distribution: It is originated from the dorso-lateral side of the midbrain and innervates the eye muscles.
Functions: It controls the rotational movements of eye muscles.
V. Trigeminal
Origin and Distribution: It is originated from lateral side of the medulla obolongata and divides into the following three branches and extended to the different organs.
(i) Opthalmic: It innervates the eye lid and the mucus membrane of the nazal cavity. It is sensory in nature.
Functions: It transmits senses from the eye-lid and the mucus membrane to the brain.
(II) Maxillary: It is extended to eye-lid, upper and lower jaws. It is sensory in nature.
Functions: It transmits senses from the eye-lid, upper and lower jaws to the brain.
(III) Mandibular: It is extended to the the muscles of the ventral buccal cavity. It is a mixed type nerve.
Functions: It controls the movement of lower jaw and transmits heat, pressure and touch senses to the brain.
VI. Abducens
Origin and Distribution: It is originated from lateral side of the medulla obolongata and innervates the lateral rectal eye muscle.
Nature: It is mixed type nerve.
Functions: It is responsible for lateral movement of the eye.
VII. Facial
Origin and Distribution: It is originated from the lateral side of the medulla obolongata and having two branches for different organs.
(i) Palatine: It is extended to the roof of the buccal cavity.
Nature: It is sensory in nature.
Functions: It is responsible for taste of food.
(ii) Hyomandibular: It is extended to the buccal cavity and lower jaw.
Nature: It is mixed in nature.
Functions: It is responsible for the taste of food and controls nick membrane.
VIII. Auditory/ Vestibulocochlear
Nature: Sensory nerve
Origin and Distribution: It is originated from lateral side of the medulla obolongata and extended to the inner ear.
Functions: It is responsible for hearing and maintains balance of the body.
IX. Glossopharyngeal
Nature: It is mixed nerve
Origin and Distribution: It is originated from the lateral side of the medulla obolongata and extended to the tongue and pharynx.
Functions: It is responsible for taste and movment of the pharynx.
X. Vagus
Origin and Distribution:It is originated from the lateral side of the medulla obolongata and it divides into the following four branches:
(i) Laryngeal: It is extended to the larynx.
Nature: It is mixed in nature.
Functions: It regulates the activities of the larynx.
(ii) Cardiac: It is extended to the heart.
Nature: It is mixed in nature.
Functions: It regulates the activities of the heart.
(iii) Gastric: It is extended to the wall of the stomach.
Nature: It is mixed in nature.
Functions: It regulates the activities of the stomach.
(iv) Pulmonary: It is extended to the lungs.
Nature: It is mixed in nature.
Functions: It regulates the activities of the lungs.
XI. Spinal Accessory
Nature: Motor nerve
Origin and Distribution: It is originated from the floor of the medulla obolongata and extended to the pharynx, larynx and neck.
Functions: It maintains the muscle movement of related organ such as shoulder and neck.
XII. Hypoglossal
Origin and Distribution: It is originated from the lateral side of the medulla obolongata and innervates the tongue and neck.
Nature: Motor nerve
Functions: It regulates the movement of the tongue.
You might also read: Endocrine Glands: Hormones, Functions and Disorders
