Blood is a fluid connective tissue which is an essential component in the human body. If the body losses this fluid, it may cause life threatening. Through the clotting mechanism, the body defends against loss of blood. In this case, different coagulation factors, vascular mechanisms, thrombocytes, enzymes, prostaglandins and proteins play important role to clot mechanism and finally stop the loss of blood. In the clotting mechanism, the cellular components are thrombocytes, various enzymes, proteins, endothelial cells and ions. Blood coagulation is also known as thrombogenesis. Blood coagulation or thrombogenesis is a complicated process by which the blood take shape clots to block and afterward rebuild an injury/wound/cut and cut the bleeding.
It is a basic piece of hemostasis preventing blood loss from damaged veins. In hemostasis, a damaged vein or blood vessel wall is stopped by a platelets and a fibrin-containing clot to stop the bleeding so that the damage can be refurbished.
Blood coagulation is a complex series of events that requires exacting chemical balances. Thirteen proteins in the blood plasma, called coagulation factors or clotting factors respond in a complex casecade to form fibrin strands which strengthen the platelets plug. The coagulation factors are shown in the following table:
| Factor Serial No | Name of Factor |
|---|---|
| I | Fibrinogen |
| II | Prothrombin |
| III | Thromboplastin |
| IV | Calcium ion |
| V | Proaccelerin |
| VI | Does not exit |
| VII | Proconvertin |
| VIII | Antihaemophilic factor A |
| IX | Chrismas factor |
| X | Antihaemophilic factor B |
| XI | Antihaemophilic factor C |
| XII | Hagman factor |
| XIII | Fibrin stabilizing factor
Laki-Lorand factor |
The clotting mechanism can be described in the following 2 stages:
Primary Hemostasis: In this case, a weak platelet plug happens. In the injury site, wall of the blood vessel constricts which helps to reduce the flow of blood. Besides this, platelets plug accumulate to the injury side.
Secondary Hemostasis: In this case, weak platelet plug stabilizes for clotting blood by the formation of fibrin network. Blood clotting occurs in the presence of different substances, known as clotting factors.
Blood Coagulation Process
- Immediately after injury ,vascular constriction occurs at many site which limits the flow of blood to the area of injury. Coagulation of the blood is initiated by the blood platelets.
- At injury site both injury tissue and platelets produce thromboplastin enzyme in presence of tissue factors and Ca++.
- In presence of VII, VIII, IX, X and Ca++ thromboplastin acts on plasma protein prothrombin which then transform into active thrombin. The thrombin forms a temporary platelets plug at injury site.
- The thrombin react with plasma protein fibrinogen and transformed it into an insoluble fiber like structure the fibrin monomer.
- Fibrin then forms an intricate network of threadlike structures called fibrils or fibrin polymer and causes the blood plasma to gel. Factor XIII is formed that links the fibrin strand together to strengthen the clot.
- To form the blood clot, blood plasma and the blood cells are entangled in the network of fibrils. Thus complete a blood coagulation process. Human coagulation time is usually 4-5 minutes.
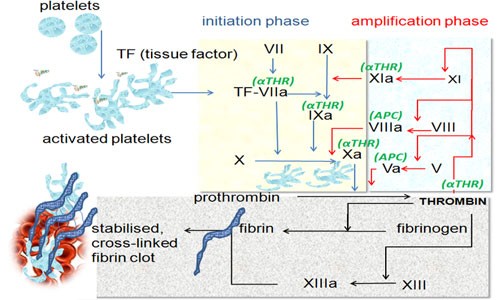
Image Showing Blood Coagulation Process: Image credit: wikimedia.org
Why blood does not clot inside the vascular system?
Blood does not clot inside the vascular system due to the following reason:
- Body always maintains continuous speedy movement of blood.
- Human blood and other tissue have 50 different types of factors or components that affect the blood clotting mechanism. These are categorized into the following groups:(a) Procoagulant factors- influence blood clotting; (b) Anticoagulant factors- prevent blood clotting. Blood clotting depend on balance between these factors. Normally anticoagulant factors dominant over procoagulant factors result on clot.
- Smoothness of the endothelium which prevent contact activation of the clotting factors.
- Presence of natural anticoagulants like heparin.
- Always removal of activated clotting factors by liver.
Any lesion/wound/cut of blood vessel influences procoagulant factors of injury site to become active and they immediately exceed the supremacy of anticoagulant factors. Thus begin coagulation.
The clear, pale yellow liquid that separates from the clot in the coagulation of blood is called blood serum. It has the same components of plasma except these clotting factor involved in clotting process like fibrinogen, factors II, V, and VIII.
