Ecosystems are of two main types such as terrestrial ecosystem and aquatic ecosystem. In this case, terrestrial ecosystems constitute the land masses which cover about 28% of the surface of the Earth. Some notable examples of terrestrial ecosystems are tundra, desert, alpine regions, rainforest etc., while the aquatic ecosystems are found in water environment that covers more than 70% of Earth’s surface.
The notable aquatic ecosystems are ponds, lakes, rivers, bogs, canals, streams, wetlands, swamp, estuaries, and ocean, etc. The aquatic ecosystem provides the habitat for various animals, plants, and microbes that are water dependents.
Types of Aquatic Ecosystem
There are different types of aquatic ecosystems:
Freshwater Ecosystem
Freshwater ecosystems include lakes, ponds, wetlands, streams, swamp, rivers, bog, and temporary pools. These cover about 0.8% of the earth surface. These ecosystem provide habitat for 41% of the world`s fish species.
The freshwater ecosystems are of the following three basic types:
- Lantic
- Lotic and
- Wetlands
Lentic Ecosystems
Lentic ecosystem includes standing water bodies. The examples of lentic ecosystems are ponds, lakes, ditches, seasonal pools, basin marshes etc. Among them, lakes have deep waters which influence by light while ponds support a wide range of water plants due to their more light penetration. Besides, algae, shrimps, crabs, frogs and salamanders are the important biotic factors of lentic ecosystem.
Lotic Ecosystems
These are rapidly flowing water bodies where unidirectional water movements are available. They have faster moving turbulent waters which contain high concentrations of DO (dissolved oxygen). These water bodies support wide range of biodiversity. These ecosystems include creek, rivers, brook, streams, spring, etc.
They provide suitable habitats for numerous species including mayflies, beetles, stoneflies and different species of fishes such as eel, trout, minnow, and different anadromous fish, etc. At present, these ecosystems are degraded through various environmental threats such as over extraction of water, dams, pollution and various introduced species.
There are two main zones of lotic ecosystems such as rapids and pools. The rapid zones have fast water flow with clear bottom while the pools are deeper areas which contain slower currents with silt builds up.
Wetlands
Wetlands are the water bodies which contains large varieties of animals and plants. It is the most well productive natural water bodies that provide habitats for large numbers of animal and plant species. It is dominated by vascular plant species due to its high productivity. In this ecosystem, animal lives include invertebrates such as damselflies, dragonflies, various birds’ species and lots of fishes, mammals, etc.
Wetlands are of main four types which include: marsh, swamps, bog and fen. In many cases, wetlands are converted into dry land that has dykes and drains. It is also used for the purpose of agriculture which provide the cultivation of rice and meet the diet of half the world`s population. It gives the benefit to humanity by filtering water, and also helps in storm protection and flood control.
Marine Aquatic Ecosystem
Marine ecosystem is the largest aquatic ecosystem which covers about 71% of the Earth`s surface. It contains about 97% water of the planet. This ecosystem contains about 85% of the dissolved materials such as sodium and chlorine.
This ecosystem has many zones, among them oceanic zone is the largest open zone which provides habitats for many aquatic animals such as sharks, whales, and various fish species. The benthic zone contains many invertebrates while the intertidal zone contains high and low tides.
Various dinoflagellates, brown algae, cephalopods, corals, echinoderms, shellfish such as crabs,, shrimps, lobsters, snails are also found in marine ecosystem.
Components of Aquatic Ecossytem
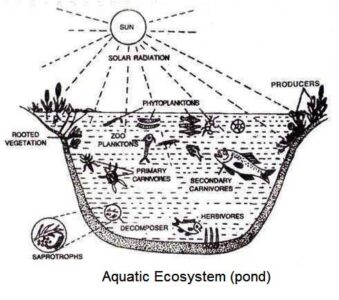
A pond is the typical aquatic ecosystem which comprises of four components. These include:
- Abiotic substances
- Producers
- Consumers and
- Decomposers.
Abiotic Substances
The abiotic substances are both inorganic and organic. The chief inorganic substances are H2O, CO2, O2, N2, Ca, P, etc. These substances in a state of solution or solubility are available for the nutrition of organisms from the environment.
Producers
The producers in a pond are mainly of two types such as (a) relatively larger plants that grow in shallow water; such plants may be rooted (Vallisneria. Hydrilla, etc) or free floating plants, such as pistia, water hyacinth, etc. (b) Minute floating plants, mainly algae constituting the so called phytoplankton. These are distributed throughout the pond as deep as light penetrates. The phytoplankton is much more important than the rooted plants in the production of basic food for the ecosystem.
Consumers
The consumers are primary, secondary and tertiary. The primary consumers feed on plants which act as producers. These are of two types: (a) Zooplankton (b) benthos. Amoeba, Daphnia, Cyclops, Diaptomus, Bismina etc constitute the zooplankton while snails, small fishes, chironomus larvae, constitute the benthos. The secondary consumers are carnivorous which feed on the plant eaters such as prawn, some fishes. The tertiary consumers eat primary consumers such as Walloga attu, Channa spp, snakes, etc.
Decomposers
Different types of aquatic bacteria and fungi act as decomposers. They are more abundant in the bottom mud rich in dead decayed plant and animal accumulation. By the action of aquatic microorganism, the dead bodies are rapidly decomposed and much simpler substances released for future use of the autophytic plants.
Plankton and Benthos
These are two major life forms in water. The organisms which are more or less dependent on water currents or wind action for their movements are called plankton. Phytoplankton are free floating plant organisms. Organisms attached with or resting on the bottom or living in the bottom sediments are called benthos or bottom forms.
Functions of Aquatic Ecosystems
Aquatic ecosystems show many beneficial environmental jobs. They make water purification, recycle nutrients, recharge ground water, prevent floods and also offer habitats for aquatic wildlife. It also provides human recreation and use as the tourism industry in coastal regions.
