Like other animals, fish need food to grow and survive. Fish food is the food that is consumed which results in growth, energy production and reproduction of the fish. Food plays an important role in fish breeding. Eating a balanced diet accelerates the growth of the fish and the fish reach sexual maturity in time. As a result, the reproductive glands of the fish are fully developed and the production of eggs and sperm is increased. Fish need a lot of energy for various important processes of life, such as blood circulation, respiratory management, hypertension control, suspension and submergence. Fish get this energy from food taken.
Types of Fish Food
There are different types of fish food in the water such as dissolved nutrients and different types of plants and animals. Details about direct nutrient intake are not known, but some fish have been found to absorb glucose directly from water. There are many primary and secondary constituents and ions that are dissolved in water and taken to the digestive tract by the fish directly through the gills or with food. Some fish absorb calcium ions to form fibers and bones through the alimentary canal. Similarly some amino acids are also absorbed. Different fish eat different types of food. Some fish eat only plant material while some fish depend on animals for food. Most fish take in protein, sugars, fats, vitamins, etc., and ingredients from both plant and animal sources for their growth and well-being.
These fish foods come from two main sources, namely-
(1) The environment in which fish live, i.e. from the aquatic environment and (2) Outside the aquatic environment i.e. from the land surface of the earth.
According to this difference in food sources, fish food can be mainly divided into two types, viz
- Natural food
- Supplementary feed
Natural Food
Water is the means of sustaining the life of fish. The foods that are naturally produced in the water of a reservoir are called natural fish food. Plankton, aquatic insects and plants, aphids, organic matter at the bottom of ponds, etc. are natural food for fish. Natural food is the main source of food for fish to survive. The adequacy of natural food in a reservoir depends on the initial productivity of that reservoir.
Supplementary Food
In addition to providing natural food for higher production, some food is provided from outside the reservoir. These foods given from outside are called supplementary food. Rice husk, wheat bran, mustard oil cake etc. are supplementary food for fish.
In addition to the above methods, fish food can also be classified in the following ways, viz.
- Plants food
- Animal food
- Mixed food
- Prepared food
Plants Food :Foods obtained from plants or vegetable sources are called vegetable foods, such as phytoplankton, grasses, soft aquatic plants, rice husk, cornmeal, mustard oil cake, wheat bran, etc.
Animal Food: Food derived from animals or animal sources is called animal food, such as zooplankton, small aquatic insects, cattle blood, silkworms, fish meals, etc.
Mixed Food: Mixed food is food that is made by mixing food of plant and animal or both sources together, such as rice husk, cattle blood, and decomposed organic matter at the bottom of the pond.
Prepared Food: Prepared food is a balanced diet that is made by mixing different food ingredients together. Food is produced in the form of granules, pills or pellets. There are different types of prepared food available in the market now. Such as- starter, grower etc.
Different species of fish have different diet and food intake. Nikolsky (1983) divided fish food into four categories, viz
Basic Foods: Basic foods are the foods that most fish eat. It is usually included in most of the fish diet.
Secondary Foods: Sometimes fish consume small amounts of food which is related to basic food elements. Such food forms the secondary food of fish.
Incidental Foods: An ingredient that rarely enters the digestive tract to form such food.
Obligatory Foods: The foods that fish consume due to lack of basic food in adverse conditions are known as compulsory foods.
Artificial Fish Feed
Artificial fish food is a type of substance that helps fish or shrimp growth, regulate health, produce heat and energy, and reproduce after being fed as a natural food supplement. In modern aquaculture, fish feed is an integral part of a source of nutrients and energy for the growth, reproduction and health of fish.
Artificial Fish Feed Types
Artificial fish food is usually prepared as floating or buoyant or sinking food. Both types of food help in the satisfactory growth of fish but some fish species prefer floating food while some species prefer drowning food. Shrimp do not eat floating food but most fish species are quite adept at eating floating pellets. It is quite expensive as the production cost of floating food is high. One of the advantages of this type of food is that the fish farmer can easily observe the food intake of fish directly and can also determine the rate of food accordingly. It is very important to determine whether the rate of food intake is too high or too low for maximum growth of fish and food utilization efficiency.
Variations in the size of the fish diet are observed. In particular, it ranges from a fine piece to a large pellet. The size of the pellet is usually 20-30% of the mouth of the fish species. In order to eat small size pellets, the fish has to find a large number of pellets, which consumes a lot of time and energy. So the pellets are usually of medium size.
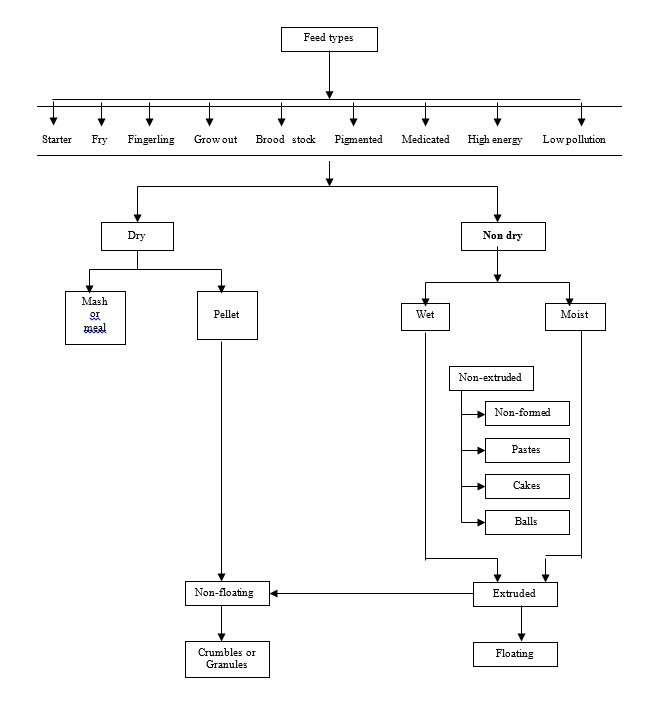
Different types of artificial food are used in intensive and semi-intensive fish farming. Two types of artificial foods are commonly used, viz
- Dry Feeds
- Non-dry feeds
1. Dry Feeds
This type of food is made with dry food ingredients or a mixture of dry or moist ingredients. Usually this type of food is not completely moisture free, it usually contains 8-10% water and it depends on the environmental conditions. This type of food is usually free of bacterial infections. Such food is divided into two types, viz
(A) Mashes or Meals: Foods that are made with very common dry food ingredients are called Mashes or meals.
(B) Pellets: Foods that are dry and have a certain size are called pellets.
Table: Formula for making dry food of shrimp (Penaeus monodon)
| Ingredients | Amount(%) |
|---|---|
| Shrimp meal | 15 |
| Fish meal | 30 |
| Soybean meal | 15 |
| Rice bran | 15 |
| Wheat flour | 15 |
| Starch | 5 |
| Oil Fish liver and soybean oil(1:1) | 4 |
| Vitamin/mineral mixed | 0.95 |
| Vitamin C | 0.05 |
Source: From New 1990
Source: From New 1990
2. Non-dry Feeds
There are usually two types of non-dry feeds, such as wet or moist. Usually wet food is made up of different types of wet ingredients such as fresh or frozen, whole, shredded or abandoned fish, other wastes including cattle slaughter blood and non-dry vegetable ingredients etc. The fish used to make wet food are herring, caplin, mackerel, blue whiting and sand lance. This type of food is more or less made from squid or other marine animals. This type of food contains 45-70% moisture. The use of such foods has declined to a large extent due to the increase in the production and use of formulated foods. Wet food is mainly used for certain marine species. The harmful side of such food is that it contaminates the water. As a result of consuming such food, many disease germs are transmitted through it. Due to the variation in the size of such food, more food is wasted which contributes to water pollution, so the use of such food is regulated in different countries, especially on freshwater farms.
Moist food is made with a mixture of dry and wet ingredients or when it is made with dry ingredients it is mixed with water. All these foods contain 18-40% moisture. Some species of fish prefer moist foods to dry foods. This type of food is widely used in salmon hatcheries.
Non-dry foods, especially moist and wet, tend to be pellet, ball or cake shaped. Both types of food are made with a combination of vitamins, minerals, oils and additives.
Table: Common carp’s ingredients and proportions needed to make moist food for common carp
| Food Ingredients | Amount (%) |
|---|---|
| Pasteurized fish (Herring, caplin) | 44 |
| Fish meal | 22 |
| Soybean meal | 12 |
| Wheat flour | 14.1 |
| Choline chlorode | 0.4 |
| Vitamin premix | 1 |
| Mineral premix | 0.5 |
| Fish oil | 6 |
Commercial Fish Feed Types
Food is classified based on the stages of the fish’s life cycle. These types of food are of the following types, namely: starter feed, fry feed, fingerling feed, grow-out feed, brood stock feed, etc.
The above five types of food are used to increase the production of cultivable species. Starter and fry feed are basically the same type while grow-out and brood stock food is also the same type of food. In addition to these foods, medicated feed, low pollution feed, high energy feed, pigmented feed, etc. are used in different countries to increase fish production and quality.
Starter Feed: This type of food is nutritious, easily digestible and of suitable size. The type and ingredients of such foods vary depending on the size of the fish and the amount of nutritional needs. Usually this type of food is made up of fine pieces. Such food is provided in the larval stage or when the fish first takes food.
Fry Feeds: This type of food contains high levels of protein (50-55%). This type of food is also formed into fine pieces. This type of food is used in the fry stage of the fish life cycle. At this stage, high levels of protein and energy are required for the rapid physical growth of the fish.
Fingerling feeds: These foods contain less protein (45-50%) than fry and starter feeds. Such foods range in size from fine pieces to pellet-shaped. Such formations usually depend on the cultivable species and their size.
Table: Ingredients and quantity of salmon fry and fingerling food
| Feed ingredients | Amount(%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Fry | Fingerling | |
| Fish meal | 65 | 61.4 |
| Blood meal | 2 | 1.9 |
| Minced milk powder | 1 | 1 |
| Powder made from milk | 1 | 1 |
| Food made from grass | 1 | 1 |
| Food made by sea weeds | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Soy lecithin | 1 | 1 |
| Wheat flour | 13.5 | 12.8 |
| Fish oil | 11 | 16.5 |
| Lime | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Salt | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Vitamin and mineral premix | 2 | 1.9 |
Grow out feeds: This type of food is used during the growth of fish. Such foods contain high levels of protein and sugar. Protein is used in such foods not only for metabolic functions but also for physical growth. Such foods tend to form fine pieces.
Brood stock feeds: This type of food contains only high levels of protein. Commercially, such foods usually contain vitamin C, vitamin E, pigment and other ingredients. The rate of physical growth decreases during sexual intercourse and the growth of the genitals accelerates until reproduction. For this reason, such foods are used to meet the nutritional needs of breeding fish.
Product quality feeds: This type of food is used to increase the quality of the fish produced. Such food is used in the vicinity of fishing to increase the consumer’s acceptability. Some foods use carotenoids to enhance the color of the meat. Product quality feeds are mostly used for highly valued species.
Medicated feeds (Product quality feeds): When the fish reduces or stops eating, it should be understood that some or the other problem has occurred. Such behavior is caused by disease or water pollution. In this case, different types of medicines are approved by the FDA. Moreover, various types of medicated food for diseased fish are also available in sufficient quantity in the market. Although it is a very easy way to treat fish with such food, it must be done very quickly and early because sick or weak fish usually stop eating quickly.
Antibiotics are used in medicated feeds to treat bacterial diseases of fish and shrimp. Scott (1993) outlines a number of principles for the use of medicated feeds in fish farming, including:
- Use antibiotics only if the bacterial infestation of fish is high;
- To start treatment as soon as possible after taking a bacterial test sample;
- The use of antibiotics to preserve the common bacterial environment;
- Avoidance of antibacterial treatment;
- To ensure the appropriate tissue level and apply the correct dose at the appropriate time;
- To apply prevention policy based on the type of antibacterial agent.
Pigmented feeds: Carotenoid dyes are used in pigmented feeds to make the color of fish flesh pink-red. This type of food is also used in shrimp farms to create the right color of shrimp shells. Synthetic carotenoids such as astazanthin and canthazanthin are used in food at the rate of 100 mg / kg.
High energy feeds: These foods contain 15-30% protein which increases the total energy of the food and increases the physical growth of the fish. Such foods are high in protein and lipids, which increases the cost. Eating such food at a higher rate increases the amount of fat in the muscles of the fish and as a result the quality of the fish decreases in many cases.
Low pollution feeds: This type of food is prepared in a special way where the water holding capacity of the food is high and the digestion of sugars is increased. This type of food uses high quality food ingredients that are completely digestible and excrete very little stool, resulting in minimal contamination.
