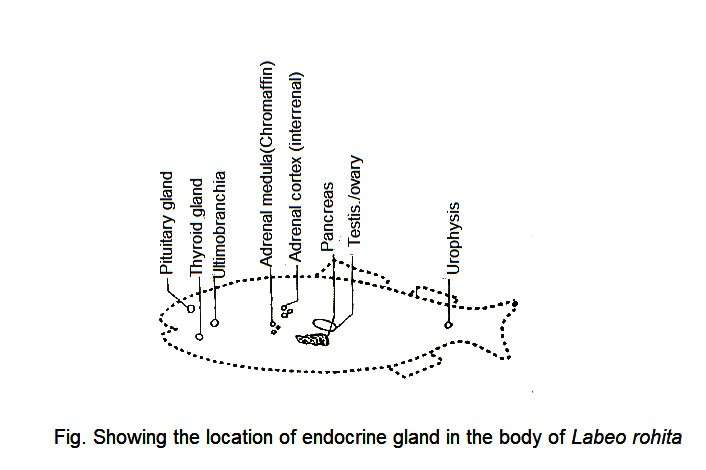
Hormones are secreted from the ductless glands, which are considered to be the regulators and stimulants of all the biological functions of the animal body. These ductless glands are called endocrine glands and the system consisting of glands is called endocrine system. Endocrine gland acts on target organ and controls their various physiological activities such as growth, digestion, metabolism, reproduction, development, etc. Labeo rohita (Rohu fish), like other vertebrates, has a number of endocrine glands. The major endocrine glands present in the body of Labeo rohita are:
- Pituitary
- Thyroid
- Adrenal and
- Thymus
Pituitary gland
The pea-shaped single pituitary gland is attached to the infandibulum by stalk located between the two segments, known as lobi inferioris of the fore brain of the Labeo rohita. The gland is divided into 3 segments or lobes. This gland is also called the regulator of glands or master gland. Several hormones are secreted from each segment of the pituitary gland. Notable among these hormones are:
(a) Growth hormone (GH)
(b) Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
(c) Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
(d) Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
(e) Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
Functions of Pituitary gland
- Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) helps to regulate body growth. It also helps to enhance the secretion of hormone from thyroid gland.
- Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) helps to control the gonadal hormone secretion. It also helps in spermatogenesis and oogenesis.
- Growth hormone (GH) helps to increase the body growth of the fish.
- Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) helps to enhance the secretion of corticotropins from adrenal gland.
Thyroid Gland
In Rohu fish, there are two thyroid glands. They are located at the front end of the body where the ventral aorta divides into two. The thyroid gland secretes hormones called thyroxin, calcitonin and tri-iodothyronine. All these hormones help in metabolism and regulate the development of fish.
Function of Thyroid Gland
- Hormone of thyroid gland helps in osmoregulation.
- It helps in maturation.
- It helps to enhance the formation of bone and scale.
- It helps to influence the fish migration.
- It helps in nitrogen metabolism.
Adrenal Gland
This gland is located in the body cavity just behind the kidney of the Rohu fish. The gland is divided into two parts called cortex and medulla. A few hormones are secreted from these two parts. These include cortisone, aldesterone and androgens. These hormones help in regulating the metabolism as well as the sexual maturity of the male fish.
Functions of Adrenal Gland
- Hormone from adrenal gland helps in metabolism of carbohydrate, electrolyte.
- It helps in sexual maturity of the male fish
- It helps to store of fats.
- It also helps in protein formation.
- It accelerates the metabolism of water.
- It also accelerates the retention of sodium ion.
Thymus glands
Each gill sac contains the thymus gland as a degenerating organ. In this case, they are located in the dorsal edge of the each gill arch. These glands secrete hormones such as thymosin that make lymphocytes and antibodies. It also aids in physical growth of Labeo rohita.
Apart from the above endocrine glands, some of the organs present in the body of Rohu fish that secrete hormones. These organs are: pancreatic islands, gonads (testes and ovaries), Corpuscles of Stannius. In addition, the anterior part of the tail of the rohu fish has an endocrine gland called urophysis. These glands secrete hormones that help control the osmoregulation of fish
Pancreatic Islands
It is located in the pancreas, and it is mesodermal in origin. It produces two types of hormone such as insulin and glucagon. They help in carbohydrate metabolism
Gonads (Ovaries and testes)
It is located in the body cavity of fish and mesodermal in origin.
Functions of Gonads
- Testosterone from testes help in development of the male reproductive system.
- Estrogen accelerates the growth and development of the female reproductive system of fish.
- Progesterone helps to stimulate the secretion of pancreas. It also helps to maintain electrolyte.
Urophysis
It is found at the end of the spinal cord of Labeo rohita. It secrets eurotensin-1 and eurotensin-2. They regulate the metabolism of various ions and water.
Corpuscles of Stannius
It is located in the posterior part of the kidney which is mesodermal in origin. It maintains the electrolyte homeostasis.