On the basis of internal structure, cells are of two types: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells are simple and small in size while eukaryotic cells are complex and large in size. Eukaryotic cells have true nucleus and nucleolus with different types of membrane-bound cell organelles such as Endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi body, Mitochondria etc. Well defined nucleus is absent in prokaryotic cell but it contains DNA molecule which is placed in the cell, known as nucleoid. Differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are stated in the following table:
|
Features |
Prokaryotic cell |
Eukaryotic cell |
|---|---|---|
|
1. Structure |
Simple, usually unicellular; |
Complex, usually multi-cellular, some cyanobacteria may be multicellular); |
|
2. Size |
Smaller; 0.5 –10 µm in diameter; |
Larger; 10.0-100 µm in diameter; |
|
3. Plasma membrane or Plasmalemma |
Present, generally contains no sterols; |
Present, contains sterols; |
|
4. Cell wall |
Generally present, composes of peptidoglycan or mucopeptide (polysaccharide); |
Absent in animal cells, present in plant cells; composes of cellulose (polysaccharide). |
|
5. Capsule |
Present, made up of mucopolysachharide; |
Absent; |
|
6. Cytoplasm |
Present; |
Present; |
|
7. Endoplasmic reticulum |
Absent; |
Present; |
|
8. Mitochondria |
Absent; |
Present; |
|
9. Golgy body |
Absent; |
Present; |
|
10. Chloroplast |
Absent; in some prokaryotic cell, chromatophores are present; |
Present in plant cell; |
|
11. Ribosome |
Present; two parts but both are small; |
Present; two parts, large and small; |
|
12. Lysosomes and peroxisomes |
Absent; |
Present; |
|
13. Nucleus |
Absent; but contains central component known as nucleoid; |
Present; contains true nucleus; |
|
14. Nuclear membrane |
Absent; |
Present; |
|
15. Nucleoli |
Absent; |
Present; |
|
16. Chromosomes and its number |
Present; single in the nucleiod; |
Present; multiple in number; |
|
17. DNA |
Present but naked; |
Present but complex with protein; |
|
18. Shape of DNA |
Circular, double-stranded DNA; |
Linear, double-stranded DNA; |
|
19. Exocytosis and endocytosis |
Absent; |
Present; |
|
20. Cell division |
Amitosis, simple fission; |
Mitosis and meiosis; |
|
21. Transcription and Translation |
They occur together; |
Transcription occurs in the nucleus while translation occurs in cytosol (intracellular fluid or cytoplasmic matrix); |
|
22. Flagella |
It is simple in structure and composes of protein, flagellin. |
Complex with 9+2 structure; composes of tubulin and other protein; |
|
23. Vacuoles |
Present; |
Present; |
|
24. Pinocytosis |
Absent; |
Present; |
|
25. Microtubules |
Absent or rare; |
Present; |
|
26. Example |
Animals and plants |
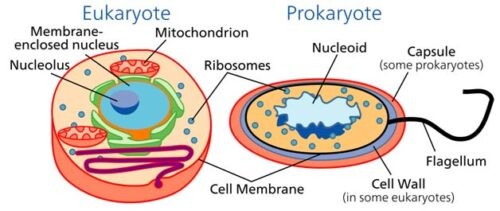
Image showing Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells
Also read: Difference between Mitochondria and Chloroplast

