The cell division is the process by which organisms generate new cells. By this process, a single parent cell divides and creates identical daughter cells. During cell division, the parent cell duplicates its genetic material (DNA) and transmits to the daughter cells.
There are three types of cell division such as amitosis, mitosis and meiosis. In this case, amitosis occurs in the lower animals like bacteria while mitosis occurs in the body or somatic cells and meiosis in germ cells producing sperm or egg cells.
Mitosis is a vital cell division process that occurs in the body repeatedly where one cell divides and produces two identical daughter cells. In this case, both daughter cells contain the same number of chromosomes or the same amount of genetic materials.
Animal mitosis and plant mitosis are the reproductive nuclear divisions which occur in animals and plants, respectively. During the mitosis, the newly produced cells contain the same number of genetic materials; as a result, the number of cells increases in the body which are crucial for growth, repair and regeneration.
There are four significant steps in mitosis such as prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. The mitotic spindle occurs in both animal and plant mitosis. In animal, mitotic spindle occurs with the support of two centrioles, but in plants, it happens through without the assistance of any centrioles due to lack of centrioles.
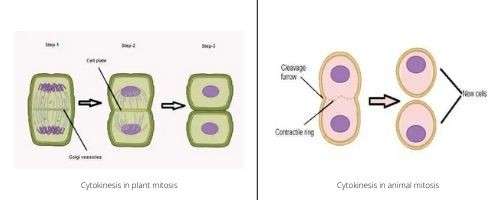
During the cytokinesis, animal cells form furrow cleavage and finally produces two daughter cells. In contrast, plant cells contain a rigid cell wall that doesn’t create furrows, but it forms a cell plate at the centre of the cells that separate the two cell components.
Besides, all the time and everywhere, animal mitosis occurs while the plant mitosis occurs in the meristem tissues.
The following table shows some significant difference between plant mitosis and animal mitosis:
|
Plant Mitosis |
Animal Mitosis |
|---|---|
|
The cells do not change the shape before cell division. |
Before cell division, the animal cells become rounded. |
|
Generally, mitosis occurs in the region of meristem tissues of the plant body. These meristem tissues are located at the tips of shoots, roots, and in the stem, between the xylem and phloem. |
Animal mitosis occurs all the time and everywhere. |
|
Plant mitosis is influenced by the plant hormone, cytokinin. |
Animal mitosis is controlled by the number of hormones but the functions of specific hormones are not yet known. |
|
Mitotic spindle occurs through without support of centrioles. | Mitotic spindle occurs in animal mitosis with the support of two centrioles. |
|
Cell plate occurs at the center of the cells. |
No cell plate occurs in the middle of the cells. |
|
In plants, centrioles, centrosomes or aster are not found. |
Centrioles, centrosomes, and asters are found. |
|
Migration of centrioles does not occur. |
Migration of centrioles occurs. |
|
In this case, solid, middle lamella occurs between the two daughter cells. |
Furrow cleavage occurs between two daughter cells. |
|
The phragmoplast enlarges which is made of actin, myosin, and microtubules and makes the cell wall in plants. |
In the telophase stage, a myosin and actin made contractile ring is present to make the two daughter cells. |
|
During cytokinesis, mid-body may be formed. |
There is no mid body. |
|
There are no major functions of microfilaments in cytokinesis. |
Microfilaments engage in cytokinesis. |
|
Spindle persists as phagmoplasts during cytokinesis. |
Spindle degenerates during cytokines. |
|
The spindle is an astral type. |
In this case, the spindle is amphiastral type. |
|
Mitotic apparatus does not consist of asters. |
Mitotic apparatus consists of asters. |
Significance of Mitosis
Mitosis involves cells division and makes new cells. This cell division process duplicates non-sex cells which is essential for growth and development.
- It helps to maintain proper cell size.
- It is responsible for the development and growth of organisms.
- It helps to distribute of chromosome equally to the newly produced daughter cell.
- It helps to replace the old and dead cells in the animal body.
- It maintains the balance of genetic material in the cells.
- It provides a definite shape of the organisms.
- It helps in the asexual reproduction of plants.
- It helps to maintain the purity of types.
- It also helps to do vegetative propagation in plants.