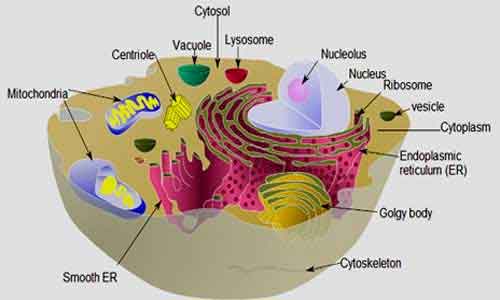
The cell is the functional and structural unit of all living organisms. The eukaryotic cells are present both in the plants and animals. The cells have various shapes, sizes, and physiology. Each cell is composed of cell membrane, cytoplasm, different organelles , nucleus, and ergastic substances. Cytosol is the part of cytoplasm which contains over 70% water.
Cytoplasm
Cytoplasm is bounded by the plasma membrane and contains the live substances. These are semi-transparent, semi-fluid, granular, vacuolated, colorless and gel-like substances.
The main and matrix component of the cell is the cytoplasm where most of the metabolic activities occur. In eukaryotic cells, the cytoplasm is placed between the plasma membrane and nuclear envelope. They make the covering of the cell organelles. A membrane-bound nucleus separates the nucleus from the other parts of the cell. Cytoplasm makes up nine-tenths of the entire cell and contains all the cell organelles, solid non-living materials, salts, stored foods, pigments, organic acids, water, etc.
Composition of Cytoplasm
Cytoplasm contains the following compositions:
- Water: about 85 %;
- Proteins: 10 – 15 %;
- Lipids: 2 – 4 %;
- Nucleic acids;
- Inorganic salts;
- Polysaccharides: smaller amounts
The cytoplasm is composed of three types of structures:
- 1The cytoplasmic matrix
- 2The cytoplasmic organelles and
- 3The cytoplasmic inclusions or ergastic substances.
1. The cytoplasmic matrix:
Cytoplasmic matrix is the homogeneous colloidal fluid. You will get the cytoplasmic matrix when you eliminate all organelles and cytoplasmic inclusion from the cell. It forms the most essential part of the cell because it provides the space for all biosynthetic and bioenergetic functions due to the presence of enzymes. The peripheral part of the matrix is comparatively non-granular, less viscous, clear and elastic in nature which is known as ectoplasm or ectoplast or plasmagel. The inner part of the matrix is granular and viscous, is known as endoplasm or endoplast. The thin layer of matrix present around the large vacuoles is known as tonoplasm or tonoplast.
2. The cytoplasmic organelles: Some specific small living organs are found in the cytoplasmic matrix of all eukaryotic cells that perform important specific functions in the cell metabolism, are known as cytoplasmic organelles.
Types of cytoplasmic organelles: There are different types of organelles, such as:
- Single membranous organelles: These include the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), the Golgi body, the Lysosome, and the vacuole.
- Double membranous organelles: These include the mitochondria and the chloroplast. They are also known as transducing organelles.
- Non-membranous organelles: The ribosome.
- Cytoskeleton and cell contractile system: These include microtubules and microfilaments
3. The cytoplasmic inclusions or ergastic substances: The cytoplasm of the cells contains a variety of non-living substances are known as ergastic substances or cytoplasmic inclusions. These substances are of three main groups:
- Reserved products: These are carbohydrates, proteins or fats. They are formed by various metabolic activities of the cells.
- Secretory products: Various products like nectar, coloring materials (pigments), hormones and enzymes, etc. are secreted by the cells, are known as secretory products.
- Excretory products: Due to metabolism, various harmful products are formed in the cell, known as excretory products. They are not secreted but stored in the cell. These products are useful to mankind such as mineral crystals, tannins, essential oils, gums, latex, alkaloids, etc.
Role of Cytoplasm
- It maintains the shape and consistency of the cell.
- It holds all of the cellular organelles outside of the nucleus.
- It contains lots of enzymes which are involved in metabolic activities.
- It provides storage space for chemical substances which are involved in the protein synthesis and anaerobic glycolysis.
- It contains lots of water with several chemical compounds which are essential for life.
- Cytoplasmic water gives the space for most of the metabolic reaction of the cell.
- Many cellular processes such as mitosis and meiosis occur in the cytoplasm.
- The cytoplasm helps to shift hormones around the cell and also dissolves the cellular waste.
- The cytoplasm also helps to transport and removal of waste products from the cells through vesicles.
- The matrix of cytoplasm provides the space for various chemical activities.
- Some metabolic activities such as absorption, assimilation of foods, synthesis or break down of various substances, etc, occur in the cytoplasmic matrix.
- The anabolic activities of the cells cause the growth of the cell.
- The cytoplasm also helps in asexual and sexual reproduction.
- It maintains the colloidal osmotic pressure of the cell.
Cytosol
Cytosol is the part of cytoplasm which contains over 70% water and it bounds the all cell organelles. It is a water-based solution which also contains the varying size of soluble molecules, proteins, amino acids, mRNA, ribosomes, sugars, dissolved ions, etc.
Properties of cytosol
- Its pH ranges from 7.0 -7.4;
- Its viscosity is similar to water;
- Its calcium ions concentration is less than 0.0002 mM;
- High amount of charged macromolecules are also present in cytoplasm.
Functions of Cytosol
- It helps to transfer signals from cell to nucleus.
- Cytosol acts as messengers. In this case, it carries a message from outside the cell, or from one part of the cell to another.
- It acts as the medium for intracellular processes.
- It contains the proteins, ions, and other ingredients for cytosolic activities.
- It also contains certain enzymes which are required for certain salt concentrations, pH levels, and other environmental conditions to work properly.
- It provides structural support of the cell and organelles.
- It creates space for chemicals to move within the cell.
Some Important Differences Between Cytosol and Cytoplasm
|
Cytoplasm |
Cytosol |
|---|---|
|
Cytoplasm is the gelatin-like, semi-transparent fluid which fills the cell. |
Cytosol is the intra-cellular fluid which is placed inside the cells. |
|
Cytoplasm is present between the cell membrane and nuclear envelope. |
Cytosol is also found within the cell membrane and nuclear envelope. |
|
It is the total content within the cell membrane and nuclear envelope. |
Cytosol is the part of the cytoplasm that does not contain any of the organelles of the cell. |
|
It contains all the cell organelles. |
It contains concentration gradients, protein complexes, cytoskeletal sieving, protein compartments , etc. |
|
Cytoplasm is composed of three chief elements such as cytosol, cell organelles and the cytoplasmic inclusions. |
The fundamental compositions of cytosol are water, dissolved ions, smaller minute molecules, large water soluble molecules, and proteins. |
|
Some important cellular activities such as cell division, glycolysis occur in cytoplasm. |
In prokaryotic cells, all types of chemical reaction occur in cytosol. |
|
Signal transduction, cytokinesis, nuclear division occur in the cytoplasm. |
Molecules transportation and signal transduction occur in the cytosol. |
Concluding Remarks
The term cytosol was first coined by H.A. Lardy in 1965. The main and matrix component of the cell is the cytoplasm. The cytoplasm is found inside the cell membrane which surrounds the nuclear envelope and the cytoplasmic organelles. It contains all the cell organelles, solid non-living materials, stored foods, organic acids, water, etc. The cell organelle less part of the cytoplasm is called cytomatrix or matrix or hyaloplasm. The central, granular mass in the cytoplasm is the endoplasm while the surrounding clear layer is known as the cell cortex or the ectoplasm.