Volvox : Characteristics, Structure, and Reproduction
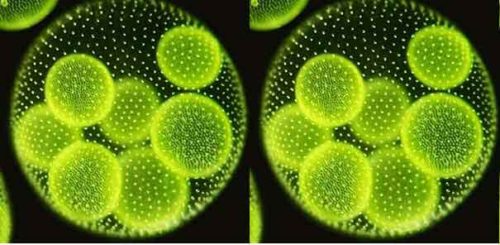
Volvox is a common freshwater free-floating chlorophytic green alga that belongs to Volvocaceae family under order Volvocales of division Chlorophyta. They occur in temporary and permanent freshwater tanks, ponds, pools, ditches, etc. There are some 20 freshwater species of Volvox which prefer to live in colonies with up to 60,000 cells by making a gelatinous … Read more