Scoliodon is an Indo-Pacific species which belongs to the family Ceacharrhinidae under order Carcharhiniformes of Class Elasmmobranchii(=Chondrichthyes). It has an elongated and spindle-shaped body which tappers at the end. The head is dorso-ventrally compressed with laterally compressed trunk and tail. The mouth is situated on the ventral side and the entire body is covered by placoid scales.
Systematic Position
- Phylum: Chordata
- Subphylum: Vertebrata
- Class: Elasmobranchii
- Order: Carcharhiniformes
- Family: Carcharhinidae
- Genus:Scoliodon
The circulatory system of cartilaginous fish such as Scoliodon is composed of blood, heart, arterial system and the venous system.
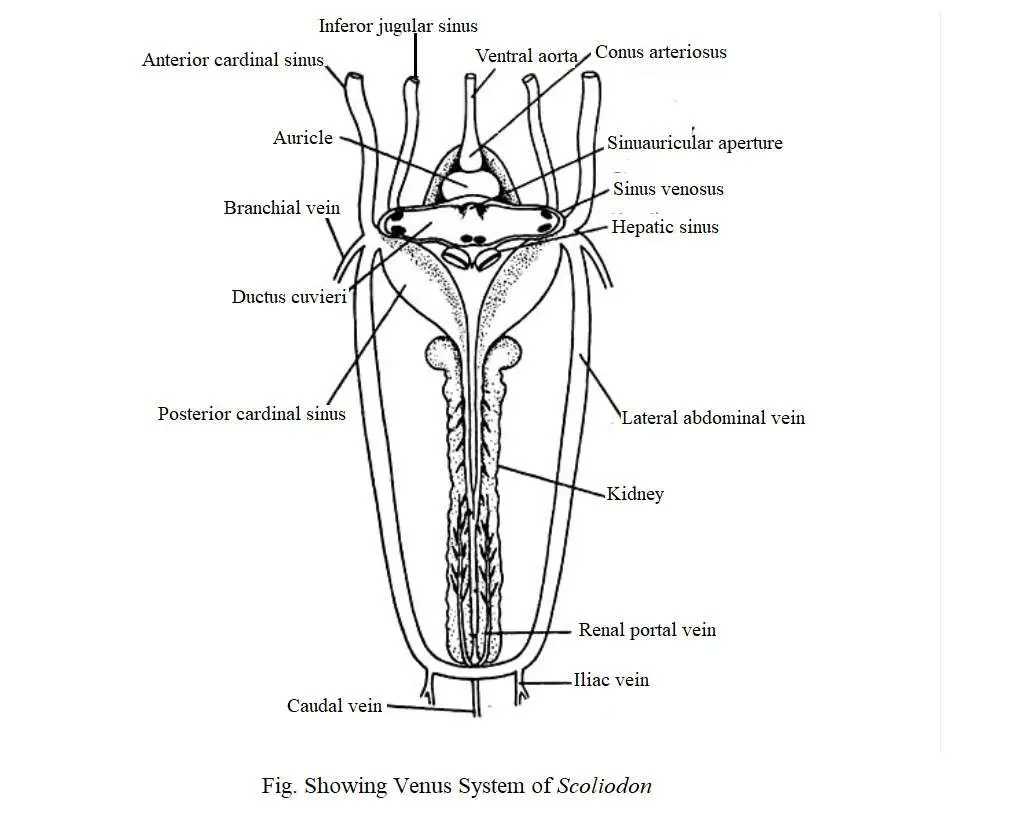
Venous System of Scoliodon
Deoxygenated blood from different parts of the body returns to the heart through veins. The structure of veins differ from the arteries which possess thin walls and frequently valves. The valves help to prevent backward flow of blood. Throughout the passages of blood, several veins form wide irregular blood sinuses without definite walls. The presence of extensive blood sinuses is a special feature of the venous system of Scoliodon. Their venous system is very complex.
The venous system of Scoliodon can be divided into the following headings:
1. Cardinal system
(i) Anterior cardinal system,
(ii) Posterior cardinal system,
2. Hepatic portal system
3. Cutaneous system.
4. Ventral system
1. Cardinal System
Blood returns to the heart from the anterior part of the body through the paired jugular and anterior cardinal sinuses. Blood from the posterior region is received through a pair of posterior cardinal sinuses. The anterior and posterior cardinal sinuses on each side combine to form a transverse sinus called the ductus cuvieri. The cardinal system can be divided into two parts, namely :
(1) Anterior cardinal system and
(2) Posterior cardinal system.
(1) Anterior Cardinal System
Blood from the head region (brain) returns to the heart through the veins of this system. It consists of a pair of internal jugular veins. Each internal jugular vein consists of the olfactory sinus, orbital sinus, post-orbital sinus, and anterior cardinal sinus.
Blood is transmitted through the anterior facial vein from the rostral region and enters the olfactory sinus. From there it goes to the orbital sinus. The orbital sinus is exposed to the anterior cardinal sinus through the post-orbital sinus. The anterior cardinal sinus enters the ductus cuvieri. The anterior cardinal sinus receives the hyoidian sinus and the 5 dorsal nutrient branchial sinus from the gills.
(2) Posterior Cardinal System
The caudal vein collects blood from the tail region and moves forward through the haemal canal. In the abdominal cavity, the caudal vein divides to form the right and left renal-portal vein, which divides into a sinusoid capillaries in the kidney.
Along its entire length, the renal-portal vein acquires small parietal veins. Renal veins receive blood from the kidneys and then unite to form the posterior cardinal sinus. The two posterior cardinal sinuses open in the ductus cuvieri.
2. Hepatic Portal System
A significant number of small veins collect blood from the alimentary canal and its associated glands and later merge to form the hepatic portal vein. Lienogastric vein, anterior and posterior gastric veins merge with the hepatic portal vein.
In fact, the anterior and posterior gastric veins combine to form the hepatic portal vein. It is divided into capillaries in the liver. Blood is collected from the liver through another set of capillaries which later merged to form two large hepatic sinuses that are exposed to the sinus venosus.
3. Cutaneous System
Cutaneous system consists of a dorsal, a ventral and two pairs of lateral cutaneous veins. The inferior lateral cutaneous vein is connected to the lateral cutaneous vein near the anterior edge of the thoracic/pectoral fin. Each lateral cutaneous vein is usually combined with the branchial vein.
4. Ventral System
Ventral system consists of two sets of veins, namely:
(1) Anterior ventral vein– which carries blood to the ductus cuvieri through the inferior jugular sinuses; and
(2) Posterior cardinal vein- it supplies blood through the subclavian vein.
The veins of each inferior jugular are composed of the submental sinuses of the lower jaw, the hyoidean sinus and the ventral nutrient sinuses from the gills. The jugular veins of each inferior are exposed in the ductus cuvieri. The subclavian vein is also exposed in the ductus cuvieri on each side.
Two large lateral abdominal veins are formed with a small caudal vein and two iliac veins. The lateral abdominal vein is connected to the posterior part by a commissural vein. Anteriorly, the lateral abdominal veins merge with the branchial veins to form the subclavian vein which is exposed to the ductus cuvieri.
You might also read: Arterial System of Scoliodon