Today, environmental pollution is a major problem which affects humans and other life forms. The earth is a vast ecosystem within it. Green plants are the primary producer in every ecosystem and constitute the functional components. They take carbon dioxide and release oxygen during the process of photosynthesis and maintain equilibrium in the atmosphere. There are also other gases like sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), ethylene, etc. in the atmosphere present in traces and are in a balanced proportion. Pollution causes negative effects on the environment, wildlife, human health, and well-being while pollutants pollute the environment.
Due to overpopulation and large scale of industrialization, some harmful components are released in the environment which disturbs the balance in nature and pollutes atmosphere and water bodies like ponds, lakes, river, etc. Other types of important environmental pollution are very frequently observed. They are commonly known as noise or sound pollution.
When the physical and biological components of the earth or atmosphere are contaminated by pollutants and adversely affect the normal environment, then it is known as pollution. In this case, naturally occurring substances are contaminated with harmful materials or foreign substances then they are considered as pollutants which cause an adverse change of natural environment.
According to Odum (1971), “pollution is an undesirable change in the physical, chemical, or biological characteristics of our air, land and water that may or will harmfully affect human life or that of desirable species, industrial processes, living conditions, and cultural assets or that may or will waste or determinate our raw material resources”.
Addition of accidental materials into the air, water or land in a concentration higher than that of the normal are detrimental to the natural quality of the environment thereby causing pollution is to make it unfit for use by undesirable elements.
Environmental pollution is the disadvantageous alteration of our surroundings, which directly affects the human being and other living organisms of the world.
Major forms of pollution include:
- Air pollution
- Water pollution
- Noise pollution
- Light pollution
- Plastic pollution
- Littering
- Visual pollution
- Radioactive contamination
- Thermal pollution
Also read:Ecology and Ecosystem
Causes of Pollution
The major causes of pollution are:
- Overgrowth of the population;
- The building of cities and town in an unscientific way;
- Using up of abundant natural resources and killing animals unscientifically;
- Misuse of technological progress in different spheres;
- Mining activities causes a release of dust and fumes into the atmosphere resulting in toxicity of air.
- Certain agricultural activities such as using of chemicals causing to air pollution.
- Poor waste disposal is a major cause of pollution.
- Use of petroleum and coal causing heavy pollution in the environment.
- Large quantities of Industrial emissions causing environmental pollution.
Effects of Pollution
- Pollution causes different types of diseases such as typhoid, tuberculosis, cancer, nerve diseases, etc.
- It causes economic loss and energy loss which results in the ultimate loss of wealth.
- Adverse air pollution can cause various diseases killing many organisms including humans.
- Decreases of various natural substances useful to human life.
- Ozone pollution can also cause different types of diseases of man including respiratory disease, chest pain, cardiovascular disease, congestion, and throat inflammation, etc.
- Water pollution causes dissuade and kill approximately 14,000 deaths per day in developing countries. In this case, it is occurred mostly due to contamination of drinking water.
- Noise pollution causes hearing loss, stress, high blood pressure and sleep disturbance.
- Lead and other heavy metals pollution cause neurological problems.
- Radioactive substances and other chemicals can cause cancer and as well as birth defects.
- Release of greenhouse gases causes global warming which affects the ecosystems.
- Soil can become infertile due to soil pollution which is unsuitable for plants and affect other organisms in the food web.
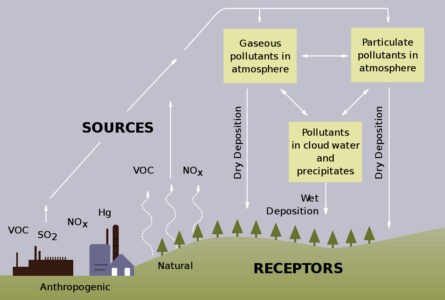
- Sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) can cause acid rain which lowers the pH value of soil and water.
- Organic pollution of water can reduce oxygen levels and finally lessen species diversity.
Pollutants
Pollution causes negative effects on the environment, wildlife, human health, and well-being. Substances which pollute the environment are known as pollutants. Odum (1971) divided pollutants into two major categories:
Non Degradable Pollutants: Substances which do not degrade or degrade very slowly in the natural environment are designated as the non-degradable pollutants such as mineral salts, aluminum cans, steel and long chain phenolic compounds, etc.
Degradable Pollutants: Those types of pollutants that break rapidly are known as degradable pollutants. The domestic wastages can be degraded by natural means or by the help of machines. Using proper methods the environment can be kept free from pollution. Some common degradable pollutants are smoke, smog, dust particles, coal tar, stored materials, metals like iron, lead, zinc, etc., nitrogen oxide, H2SO4, HCl, CO2, N2O, NH3, SO2, and other gaseous substances, different insecticides, DDT, Radioactive substances, etc.
Control Measures of Pollution
- Introducing post-combustion measures to lessen the emission of various gaseous substances such as sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matters from power stations and in large-scale industry.
- Introducing advanced emissions standards in various industries such as cement factories, glass and, chemical industry, iron and steel plants, etc.
- Improving and strengthening emission standards for road vehicles such as light- and heavy-duty diesel vehicles.
- Making compulsory checks and repairs for vehicles by vehicle inspector.
- Suppressing construction and road dust; increasing green areas.
- Open burning of agricultural crop residues should be strictly prohibited.
- Open burning of residential and household waste should be strictly banned on.
- Forest and peatland fires must be prevented using improved forest, land and water management and fire prevention strategies.
- Livestock manure management strategies should be followed. In this case, you should encourage anaerobic digestion.
- Use of private passenger vehicles should be discouraged to lessen CO2 emission. In this case, the public transport system should be encouraged.
- Introducing well-managed wastewater treatment with biogas recovery.
- You should use clean fuels like electricity, natural gas, liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) in cities.
- Introducing LPG and advanced biomass cooking and heating stoves in rural areas;
- For electricity generation, you should use of wind, solar and hydropower system.
- Encouraging the use of electric vehicles instead of diesel engines.
- Improving and enforcing energy efficiency standards for households and industries.