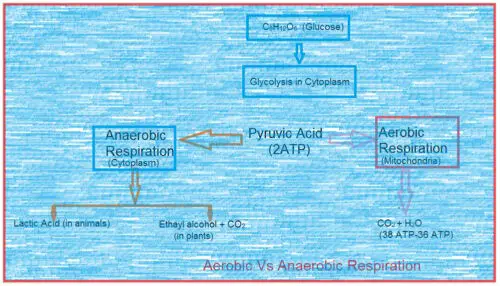
Respiration: Types and Significance
Respiration is basically an energy releasing and supplying process. It held in each cell of the plant. Its primary stages take place in the cytoplasm and secondary stages in mitochondria. Actually respiration is the set of the metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert kinetic energy from nutrients … Read more