For proper survival of the plants and animals, they have to struggle against the environment, their different factors and other living organisms. Viruses are microscopic organisms and can be seen only under electron microscope. In nature, any living organism is affected by virus, then it will take a serious turn. Viruses are mysterious biological agents which do not show any sign of life in free-state and are seen to remain as non-living things. There are million species of virus in nature, among them, about 5000 species have been described in details. The term virus is derived from a Latin word, meaning slimy liquid or poison. This term was first given by Dutch microbiologist Martinus Beijerinck. The branch of science which deals with the virus is called Virology and the specialists of this branch are designated as Virologist.
Definition of Virus
Viruses are biological agents as they exhibit characters of both non-living and living organisms. Some definitions of viruses are given below:
- Viruses are ultra-microscopic disease causing nucleo-protein agents, capable of being introduced into the living cells of specific organisms and capable of multiplying or being multiplied within the living host cells.
- Virus is a kind of micro-organism of at least less than 200 mµ in size, lives parasitically on a definite host (Bawden, 1949).
- Viruses are some ultra-microscopic entities, which multiply only after entering the cell of a specific living organism (Luria, 1953).
- Viruses are ultra-microscopic , filterable ( through bacterial filter), acellular, antigenic, obligatory parasitic, infectious, nucleo-protein particles which have the power to multiply only within the specific living host cell, lies in between inanimate and animate objects.
Salient Features of Virus
- Viruses are only visible under electron microscope, a kind of organism lies in between living and non-living objects.
- Viruses show their existence in water, land and air.
- As they are ultra microscopic particles, hence they can be filtered through the bacteria proof micro-filter easily.
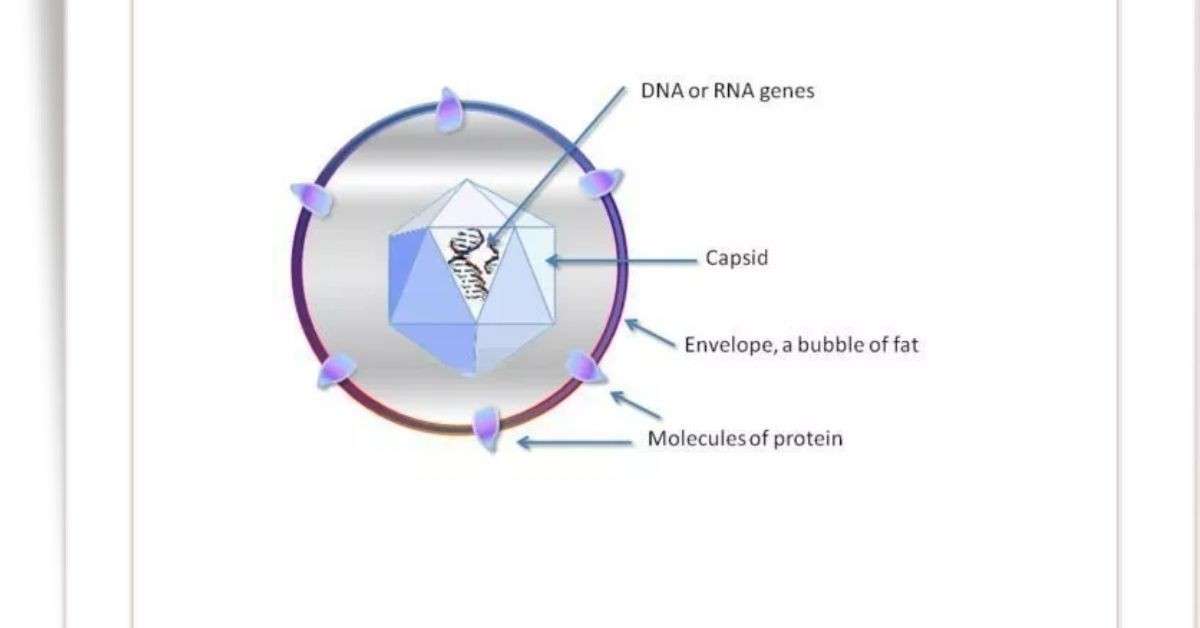
- Cytoplasm is absent within the body of viruses, hence it is non-cellular.
- Its body is composed of nucleo-protein.
- They are very infectious obligatory parasites.
- The disease producing virus particles can only multiply within living organisms.
- They do not show any sign of life in free state and are seen to remain as non-living entities.
- Any metabolic activities within the virus body are not visible.
- As sunlight has no direct influence over the viruses, hence they can resist a very high temperature.
- Viruses can be transferred from an infected body to healthy plants, animals or human beings.
- Virus contains either one type nucleic acid-DNA or RNA. Plant viruses are generally RNA viruses and animal viruses are generally DNA viruses.
- Virus reproduces only by the replication of gene or chromosome.
- Living characters of viruses are reproduction and mutability.
Nature of Virus
- Virus which lies between living and non-living objects, possess a high molecular mass of protein particles.
- They do not show any sign of life in free state and are seen to remain as non-living things.
- Nucleo-protein is the important element of the virus body, which is composed of nucleic acid and protein.
- Virus lives on the host cell totally as an obligate parasite.
- Virus can multiply and reproduce as soon as they enter within the host cells, when they are considered to be living.
- They reproduce by replication of gene or chromosome.
- Viruses are indeed smallest, non-cellular, non-cytoplasmic organisms which can pass easily through bacteria proof filter.
- Viruses liberate their own protein membrane during infection outside the host cell and pass only the nucleic acid (DNA and RNA) within the host cell for reproduction.
- Their living characters are reproduction and mutability.
- Viruses have two phases in their life cycle- intracellular and extracellular, which are noted within the host cell and outside the body of the host.
Where They Occur
- The existence of viruses is noted in aquatic, terrestrial and aerial conditions.
- Virus lives generally within the alimentary tract of human being and other animals.
- The existence of virus is also noted in different vegetables, fruits, milk and different types of foods and drinks.
- The presence of viruses is also noted within the residual product, urine, saliva, etc of a viral attacked patient.
Characteristics of Virus
Virus shows the both living and non-living characteristics.
Living characteristics are:
- Virus body contains DNA or RNA and protein.
- They can reproduce within the host body.
- They exhibit mutability and can infect other living organisms.
The non-living characteristics are:
- Virus molecules can be converted into crystals.
- The body is not covered by cell membrane.
- Virus body does not contain cytoplasm.
- They have no power of locomotion.
- They can`t respond to external stimuli.
- Virus body does not show any metabolic reactions.
- They remain inactive outside of the host body.
Size of virus
Virus particles are ultra-microscopic entities that can be seen only under electron microscope. They are very small and vary in size appreciably. The average diameter of a virus lies between 8-280 mµ. The foot and mouth disease virus of cattle is the smallest known virus which is nearly 8-12 mµ in size and the larger sized virus particles are noted in the vaccinia and Variola viruses (280-300 mµ).
The size of the tobacco leaf mosaic virus is 17 mµ. On the other hand, parrot fever virus (Psittacosis) Chlamydia psittaci is the largest among the viruses, which is a large as 450 mµ in diameter. According to Salle (1974), these are not virus. They can easily seen under a normal compound microscope. In this case, the larges virus will be Lymphogranuloma venereum (size: 300-400 mµ).
Shape of Virus
Virus body shows four different shapes such as spherical, rod-shaped, cuboidal and tadpole-like structure.
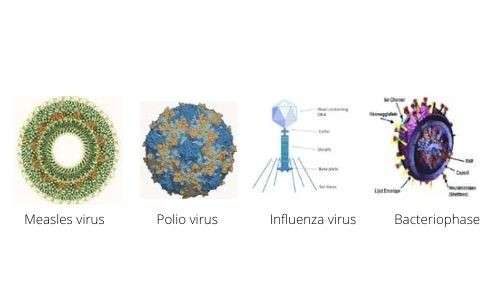
Spherical shaped virus: These type of virus are more or less round, like small golf ball such as influenza virus, Polio virus, Encephalitis virus, Tumor virus, etc. They show 18-150 mµ in diameter.
Rod shaped virus: This type of virus looks like small rod such as Tobacco mosaic virus (TMV), Mumps virus etc. They can grow 800 mµ in length and 15 mµ in diameter.
Cuboidal shaped virus: This type of virus is cubic shaped such as small pox viruses like Vaccinia and Variola, Canary pox, Herpes etc. Their size ranges between 210-305 mµ.
Tadpole shaped virus: This type of virus looks like spermatozoa or tadpole such as bacteriophase virus. They have head and tail in their body. The head measures 47-104 mµ and the tail measures 10-225 mµ.
Classification of Virus
On the basis of nucleic acid, virus is divided into two types such as:
- Deoxyvirus: They compose of Deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA.
- Ribovirus: This type of virus composes of Ribonucleic acid or RNA.
On the basis of the virus host, they can be divided into:
- Plant virus: This type of virus can reproduce within the plant body. They can cause plant diseases. Plant viruses include Tobacco Mosaic Virus(TMV), Bean Mosaic Virus(BMV), Pea Mosaic Virus (PMV), Cauliflower Mosaic Virus (CMV).
- Animal Virus: This type of virus reproduces within the animal body and can cause diseases of animal. Some animal viruses are influenza virus, Polio virus (Polio myelities), Measles virus, small pox virus (variola, Vaccinia).
- Bacterial virus: This type of virus attacks and multiply within the body of bacteria, hence it is called bacteriophase.
On the basis on Genome structure, virus is classified into the following types:
|
Virus name |
Example |
|---|---|
| RNA |
Retroviruses, Rabies virus |
| DNA | Smallpox virus, Herpesviruses |
| Single-stranded |
Retroviruses, Rabies virus |
| Double-stranded | Herpesviruses, smallpox virus |
| Linear |
Herpesviruses, Rabies virus, retroviruses, smallpox virus |
| Circular |
Many bacteriophages, Papillomaviruses |
| Genome with a single segment | Parainfluenza viruses |
| Genome with multiple segments | Influenza viruses |
On the basis on Capsid Structure, virus is classified into the following types:
|
Virus Name |
Examples |
|---|---|
|
Naked icosahedral |
Hepatitis A virus, polioviruses |
|
Naked helical |
Tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) |
|
Enveloped icosahedral |
Yellow fever virus, Epstein-Barr virus, rubella virus, herpes simplex virus, HIV-1 |
|
Enveloped helical |
Rabies virus, Influenza viruses, measles virus, mumps virus |
|
Complex with many proteins; some have combinations of icosahedral and helical capsid structures |
Hepatitis B virus, T4 bacteriophage, Herpesviruses, Smallpox virus |
According to David Baltimore Virus is classified into following categories:
| Virus Categories | Characteristics | Virus Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Group I | Double-stranded DNA | Herpesvirus (Herpes simplex) |
| Group II | Single-stranded DNA | Parvovirus (Canine parvovirus) |
| Group III | Double-stranded RNA | Rotavirus (Childhood gastroenteritis) |
| Group IV | Positive Signed Single stranded RNA | Picornavirus (Common cold) |
| Group V | Negative Signed Single stranded RNA | Rhabdovirus (Rabies) |
| Group VI | Single stranded RNA viruses with Reverse Transcriptase Enzyme | HIV (Human immunodeficiency virus) |
| Group VII | Double stranded DNA viruses with Reverse Transcriptase Enzyme | Hepadnavirus (Hepatitis B virus) |
Advantages of Virus
- Bacteriophage or T2 Virus is used in carbon cycling;
- They are used in scientific research in the field of cell biology and molecular biology;
- They are used as vectors for treatment of various diseases;
- Virus is used to deliver the gene to target cells.
- Virus plays important role in scientific researches of gene therapy.
Disadvantages of Virus
- In nature, there are many harmful viruses which can cause diseases in plants and animals. Some notable human disease causing viruses are HIV, influenza, herpes, hepatitis, Polio virus (Polio myelities), Measles virus, small pox virus (variola, Vaccinia) while in plants, notable viruses are tobacco mosaic virus, Bean Mosaic Virus(BMV), Pea Mosaic Virus (PMV), Cauliflower Mosaic Virus(CMV).
- Virus also can cause cancer in human and other animals;
- Virus transmits diseases from person to person;
You may also read: Virus Structure