Enterobius vermicularis is commonly known as threadworm and pinworm. It is found all over the world. Infection of Enterobius vermicularis in human is known as enterobiasis. It is worldwide in distribution. Particularly, it is common in children. Generally, the mature females live in the vermiform appendix and caecum.
Systematic Position
- Phylum: Nematoda
- Class: Chromadorea
- Order: Rhabditida
- Family: Oxyuridae
- Genus: Enterobius
- Species: Enterobius vermicularis
Morphology
It is a small nematode parasite found in intestine of humans. It is white in color and resembles a piece of thread. It has no buccal cavity. At the anterior extremity, a pair of cervical alae is seen. The posterior part of the oesophagous is dilated into a globular bulb that is look-like a double-bulb oesophagus. The adult male can grow up to 4 mm in length with 0.1-0.2 mm breadth.
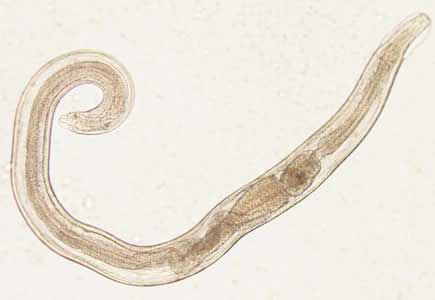
The posterior third portion of the body is curved. The body contains copulatory spicule which is exposed. The female worm is longer than the male and it can grow up to 12mm in length with 0.3-0.5 mm in breadth. The posterior portion of the female is extremely straight, tapering with finely pointed tail. The gravid females lay an average of 11,105 eggs. Male usually dies after fertilizing the female while the gravid female, after oviposit, dies within 2 to 3 weeks.
Life Cycle of Enterobius vermicularis
It does not require intermediate host to complete the life cycle. Adult worms live in the caecum. The male fertilizes the female and dies. Fertilized female then migrates to rectum and passes out of the anal orifice, especially at night and lays eggs containing a tadpole-like larva on the perianal and perineal skin.
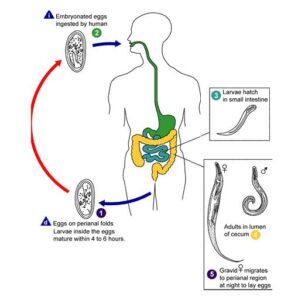
Infection occurs by ingestion of these eggs. Intense itching develops in the area. After this either (a) the patient ingests eggs from his nails and fingers contaminated from his own perineal region (direct from anus to mouth) . The cycle is repeated in the same individual or (b) another person ingests the eggs (first infection) by handling bed linens or night cloths or by taking contaminated food and drink. The egg shells are dissolved by digestive juices and the larvae develop into sexually mature adults. The cycle is then repeated.
Retrograde infection can also occur. In the larvae hatch out of eggs on the perianal skin and then migrate up within the intestine through anal orifice and develop into adult forms.
Pathogenesis and Clinical Features
Children are the usually victim. Familial infection is common. The infection may be symptomless.
- Pruritis in the perianla and perineal regions due to irritation by the worms and scratching.
- Gastrointestinal symptoms such as pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea or rarely dysentery) may develop.
- Appendicitis-worm within appendix.
- In female patients vaginal irritation, vulvo-vaginitis and urethritis.
Laboratory Diagnosis
Demonstration of eggs or adult worm from perianal region or in the stool is diagnostic.
1. Demonstration of eggs
- Adhessive surface of cellophane tape is applied to the perianal skin in the morning before defaecation or a wash. The tape is removed and placed on a glass slide and examined under microscope. This method is recommended.
- Scrapings from perianal skin by a swab with cellophane tape on tip. The tape is placed on glass slide and examined.
- Microscopic examination of stool may reveal the eggs by a direct cover slip preparation or by concentration method.
Characteristic Features of Eggs
- Eggs are colorless.
- The size varies from 50 to 60 µm by 30 µm.
- One side of the egg is flattened and other side is convex (planoconvex).
- It is surrounded by a transparent shell.
- It contains a coiled tadpole-like larva.
- It can float in saturated solution of Nacl.
2. Adult worm may be found occasionally in the stool or perianal region even by patients or parents of children.
Symptoms of a pinworm infection
- Strong itching of the anal area occurs;
- It hampers sleep due to discomfort and anal itching.
- It hampers sleep due to discomfort and anal itching.
- Pinworms are also seen in the children`s anal area.
Treatment
The following medications are used for the treatment of Enterobiasis or pinworm infection:
- Mebendazole
- Pyrantel pamoate
- Albendazole
- Piperazine
- Pyminium pamote
The following above any drug is given in one dose initially and finally, after two week later, you should take another single dose.
Preventive Measures
- Stop the biting your snails;
- You have to keep finger nails short and clean;
- You have to wash hand using warm water and soap before eating and after defecation;
- Change your underwear daily;
- You have to maintain good personal hygiene;
- Bed liners and night dress hould be washed regular basis.
- Fingers should not be kept in mouth as habit.
